The case management process is effectively applied across various fields to ensure smooth coordination and support for individuals or groups with unique needs. Whether in healthcare, social work, or legal services, case management plays a major role in providing tailored assistance and achieving positive outcomes. In this guide, we’ll break down the core of the case management process, making it easy to understand and apply.
- What is the Case Management Process
- Case Management Process Steps
- Case Management Process Template
- Who are Involved in the Case Management Process
- Importance of the Case Management Process
What is the Case Management Process
At its core, the case management process is a supportive and organized process to help individuals or groups with specific needs navigate challenges and achieve positive outcomes. It involves a dedicated professional, known as a case manager, who acts as a guide, coordinator, and advocate.
The case manager collaborates with the individuals, analyzes their needs, and develops an action plan. This plan serves as a roadmap, outlining the steps to address challenges, access necessary resources, and reach desired goals. In essence, case management is about providing focused, individualized assistance to improve well-being and facilitate success in various aspects of life.
Depending on the context, how we apply case management can be different. For example, in healthcare, case managers may help coordinate medical services for patients, while in social work, case managers might assist individuals and families in accessing social services and support. The overall goal of case management is to improve the well-being of the individual or group by providing effective and coordinated services.
Case Management Process Steps
The case management process steps can be broken down into the following steps. These steps are flexible, letting case managers go back and make adjustments when needed. For instance, if challenges pop up during implementation, it’s important to revisit the planning stage in this adaptable process.
1. Screening
Screening involves identifying potential clients and assessing their eligibility for case management services. This helps determine if more in-depth assessment and intervention are needed.
2. Assessing
The assessment phase involves a thorough examination of the client’s needs, strengths, and challenges. It includes gathering information on the client’s background, living situation, health status, and other relevant factors. This comprehensive assessment help form the basis for developing a personalized case management plan.
3. Risk Evaluation
In this step, the case manager evaluates potential risks and challenges that the client may face. This could include safety concerns, health risks, or social challenges. Understanding and identifying these risks is important for developing strategies to mitigate them and support the client’s well-being.
4. Planning
Based on the assessment and risk evaluation, a detailed plan is created. This plan outlines specific goals, interventions, and timelines to address the identified needs and challenges.
5. Implementing
The plan is put into action during the implementation phase. This involves coordinating and providing the necessary services, resources, and support as outlined in the case management plan.
6. Following-up
Regular follow-ups are conducted to monitor the progress of the individual or group. This step help make sure that the interventions are effective and allows for adjustments to be made as needed.
7. Evaluating
Continuous evaluation is important to assess the overall effectiveness of the case management process. This involves measuring progress, identifying areas of improvement, and determining if the goals are being met.
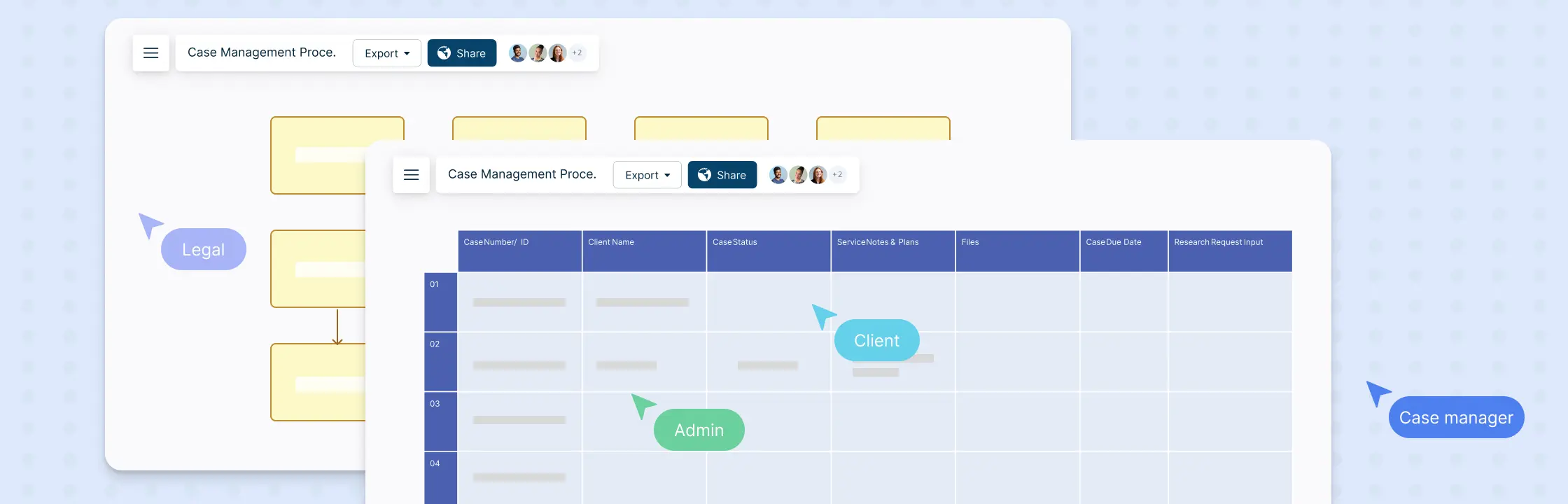
Case Management Process Template
Below is a simplified template structure that you can customize based on your specific needs and the requirements of your case management process.
Who are Involved in the Case Management Process
The case management process involves collaboration among various stakeholders. Key participants include the case manager, client, family/support system, collaborating professionals, referring agencies, service providers, administrative staff, legal representatives, advocates, community resources, educational institutions, and mental health professionals.
Effective communication and coordination among these stakeholders are essential for the successful development and implementation of a case management plan, ensuring the diverse needs of the client are addressed.
Importance of the Case Management Process
Personalized support: Case management process makes sure care plans are tailored to each person or group’s needs and circumstances.
Efficient resource utilization: It optimizes the use of resources, preventing waste and making sure that interventions are cost-effective and impactful.
Proactive issue resolution: Case management promotes proactive issue resolution by monitoring progress and identifying challenges early.
Empowerment and collaboration: Case management empowers clients by involving them in decision-making, fostering collaboration, and making sure they’re involved in their care.
Coordination of services: It makes sure that professionals and service providers work together seamlessly, so care is coordinated and integrated.
Continuous improvement: Through documentation and regular evaluations, case management supports continuous improvement, allowing for adjustments to interventions based on evolving needs.
In essence, the case management process contributes to better outcomes for clients by helping professionals navigate the varied and changing world of client care. While this post simplifies what is a case management process and its key components and steps, we hope it helps you navigate through the complexities of case management more effectively.