In any organizational setting, understanding power dynamics and influence is crucial for effective decision-making, collaboration, and achieving goals. One powerful tool that helps with navigating these dynamics is the power-influence Grid. This comprehensive guide aims to provide insights into what a power-influence grid is, why it’s valuable, how to utilize it effectively, who can benefit from it, and the various advantages it offers.
What is a Power-Influence Grid?
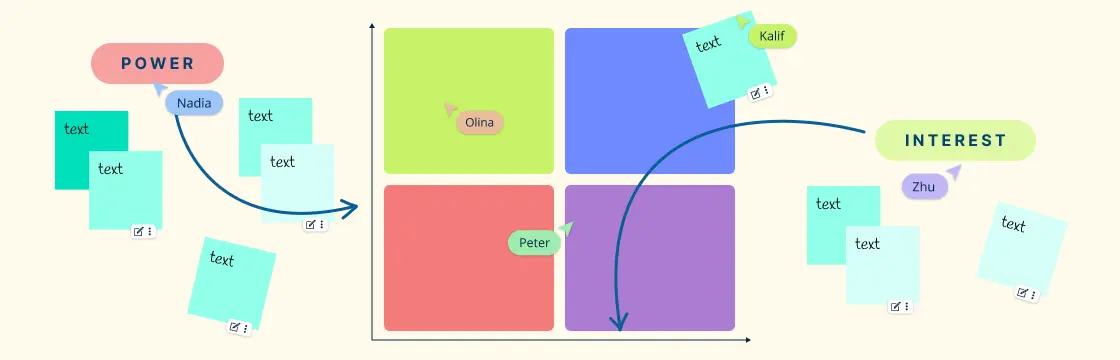
A power-influence grid, also known as a power-interest grid, is a visual representation that maps out individuals or groups within an organization based on their level of power and influence. It helps in identifying key stakeholders, decision-makers, influencers, and supporters within a network. By plotting individuals or groups on this grid, one can gain a clearer understanding of the dynamics at play and strategize accordingly.
Divided into four quadrants, stakeholders are placed according to their positioning on the axes of power/influence and interest/involvement. Stakeholders with high power and high interest are considered key players who require close management and engagement, while those with high power but low interest may need to be kept informed despite their lower level of active involvement. Conversely, stakeholders with high interest but low power can serve as advocates or supporters, while those with low power and low interest typically require minimal attention. This grid helps project managers prioritize their efforts and tailor communication and engagement strategies to meet the needs of each stakeholder group effectively.
How to Use a Power-Influence Grid?
Here’s how to effectively use a power-influence grid to gain insights into organizational dynamics, inform decision-making, and navigate complex relationships for achieving your goals.
1. Recognize relevant stakeholders
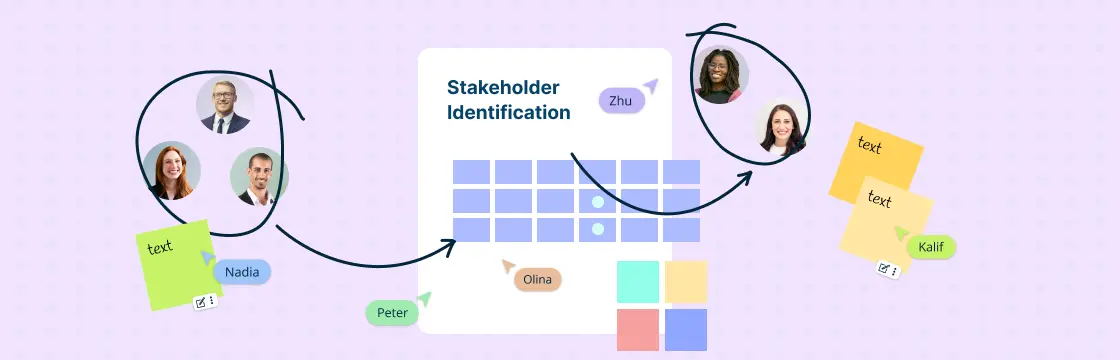
Begin by recognizing all individuals or groups who are relevant to the context you are analyzing. These could include key decision-makers, influencers, supporters, opponents, and other stakeholders with a vested interest in the issue at hand.
2. Assess power
Evaluate the power of each stakeholder based on various factors such as:
- Formal authority: Position within the organizational hierarchy, title, and role.
- Control over resources: Access to financial, human, or other resources that can influence outcomes.
- Expertise: Specialized knowledge, skills, or experience relevant to the issue.
- Access to information: Availability of crucial information or data that can impact decisions.
- Network: Connections and relationships with other influential individuals or groups.
3. Assess influence
Determine the influence of each stakeholder by considering factors such as:
- Persuasion skills: Ability to sway opinions, change minds, and mobilize support.
- Networks: Size, diversity, and strength of personal and professional networks.
- Reputation: Perceived credibility, trustworthiness, and respect within the organization or community.
- Charisma: Personal qualities that attract followership and inspire action.
4. Plot on the grid
Create a grid with two axes representing power and influence, respectively. Assign a scale (e.g., low to high) for both power and influence on each axis. Plot each stakeholder on the grid based on their assessed power and influence levels. Use symbols or colors to differentiate between different types of stakeholders (e.g., decision-makers, influencers, supporters).
5. Analyze relationships
Once all stakeholders are plotted on the grid, analyze the relationships between them. Identify clusters of stakeholders with similar power and influence levels, as well as any patterns or dynamics that emerge. Pay attention to connections, alliances, conflicts, and dependencies between stakeholders.
6. Develop Strategies
Based on the insights gained from the grid, develop tailored strategies for engaging with different stakeholders. Consider the positions of key players and the dynamics of relationships when formulating your approach. Identify potential allies, influencers to engage, areas of resistance to address, and opportunities for collaboration.
7. Implement and adapt
Put your strategies into action, engaging with stakeholders according to your plan. Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your approach, and be prepared to adapt your strategies based on changing circumstances or feedback from stakeholders.
8. Review and update
Periodically review and update the Power-Influence Grid to reflect any changes in power dynamics, influence relationships, or the context itself. This ensures that your strategies remain relevant and effective over time.
Who Uses a Power-Influence Grid?
The power-influence grid is used by a wide range of professionals and organizations, including:
- Managers and leaders: For strategic planning, decision-making, and managing organizational dynamics.
- Project managers: For stakeholder analysis and managing project stakeholders effectively.
- Consultants: In organizational development, change management, and conflict resolution processes.
- HR professionals: For talent management, succession planning, and organizational design.
- Team leaders: For understanding team dynamics and facilitating collaboration.
Benefits of a Power-Influence Grid
- The power-influence grid provides a clear visual representation of power dynamics within a group or organization, helping stakeholders understand who holds influence and authority.
- It helps with the identification of key stakeholders, decision-makers, influencers, and supporters, allowing for targeted engagement and collaboration efforts.
- By mapping out power and influence relationships, the grid helps in making informed and strategic decisions, considering the interests and perspectives of influential parties.
- It facilitates effective stakeholder management by providing insights into stakeholders’ positions and interests, allowing for tailored communication and engagement strategies.
- The grid can help in conflict resolution by identifying underlying power dynamics and relationships, enabling parties to address conflicts more effectively and find mutually beneficial solutions.
- Organizations can optimize resource allocation by focusing efforts on areas with the most significant influence and impact, ensuring resources are utilized effectively and efficiently.
How to Use Creately to Create a Power-Influence Grid
Creately offers multiple diagramming tools and templates to map out stakeholders and understand their influence, relationships, dependencies, and behavior at a glance and develop efficient strategies to further improve any stakeholder activities.
Built-in prioritization grids & brainstorming tools
Use mind map maker to create mind maps or sticky notes or other brainstorming tools to quickly brainstorm and list down project stakeholders. Visual prioritization grids to easily plot stakeholders against their power and interest to determine who has high or low power to affect your project, and who has high or low interest.
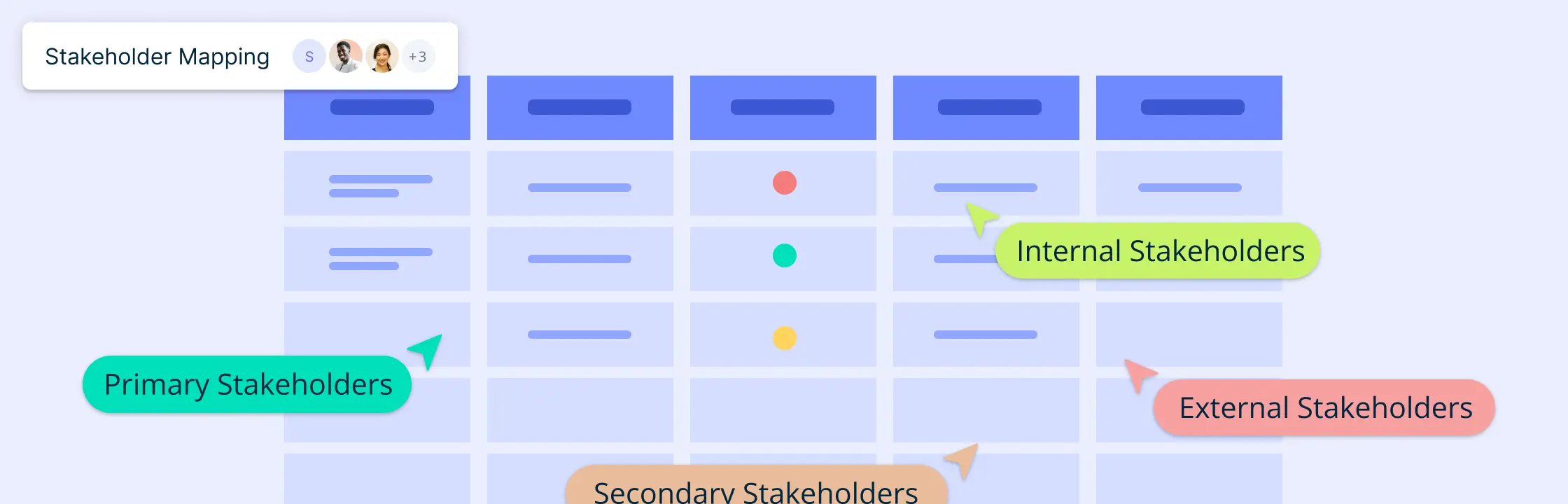
Pre-made templates
Get a head-start with multiple templates including power-influence grids, stakeholder maps, stakeholder registers and more to easily identify, analyze, prioritize stakeholders easily.
Notes and attachments
Record additional details and attach documents, files, and screenshots related to stakeholders with per item integrated notes panel and custom data fields. Or easily embed files and attachments right on the workspace to centralize information.
Real-time collaboration
Get any number of participants on the same workspace to brainstorm or present information. Collaborate with stakeholders in the project seamlessly with true multi-user collaboration features including synced previews and comments and discussion threads. Use Creately’s Microsoft Teams integration to brainstorm, plan, run projects during meetings.
In conclusion, the power-influence grid is a valuable tool for navigating complex organizational dynamics, facilitating collaboration, and achieving strategic objectives. By understanding power and influence relationships, organizations and individuals can make more informed decisions, improve communication, and effectively manage change and conflict.