Imagine you’re leading a product team at a cutting-edge tech company. Your latest innovation is poised to disrupt the market, but as you dive into development, challenges start piling up. Design changes cause manufacturing delays. Marketing is working with outdated specs. Supply chain hiccups threaten your launch date. And to top it off, customer feedback from your last product hasn’t been fully incorporated into this new design.
Sound familiar? In today’s fast-paced business environment, bringing a product from concept to market is more complex than ever. It’s not just about having a great idea; it’s about efficiently managing every stage of a product’s life cycle, from that initial spark of inspiration to its eventual retirement.
This is where Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) comes into play. It’s the strategic approach that’s revolutionizing how businesses create, develop, and maintain their products. PLM isn’t just another acronym to add to your business jargon; it’s a game-changer that can streamline your processes, boost innovation, and give you a competitive edge in the market.
What is a Product Lifecycle?
A product lifecycle refers to the stages a product goes through from its conception to its eventual discontinuation. This concept is crucial for businesses to understand as it influences marketing strategies, resource allocation, and long-term planning.
The typical product lifecycle consists of four main stages:
Introduction: The product is launched into the market. Sales are low, and marketing costs are high as companies focus on creating awareness and attracting early adopters.
Growth: The product gains traction, with increasing sales and market share. Profits begin to rise, and competitors may enter the market.
Maturity: Sales peak and growth slows. The market becomes saturated, and companies focus on differentiating their product and maintaining market share.
Decline: Sales and profits decrease as new technologies or changing consumer preferences make the product less desirable. Companies must decide whether to discontinue the product or attempt to revitalize it.
Understanding where a product is in its lifecycle helps businesses make informed decisions about investment, marketing, and innovation. It also guides product development efforts, ensuring companies stay competitive by introducing new products or improving existing ones before they reach the decline stage.
What is Product Lifecycle Management?
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is a comprehensive approach to managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its conception, through design and manufacture, to service and disposal. It integrates people, data, processes, and business systems, providing a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprises.
The History of Product Lifecycle Management
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) has its roots firmly planted in the early 1930s. Initially, it was a concept focused on integrating and managing disparate information, processes, and people involved in product development. By 1957, Booz Allen Hamilton introduced a structured five-step lifecycle approach, shaping the foundation of modern PLM.
Over the decades, PLM has significantly evolved, driven by technological advancements and the need for streamlined product development processes. Early PLM tools were heavily CAD-centric, focusing primarily on computer-aided design. However, as businesses required more integrated solutions, PLM expanded to incorporate various aspects of the product lifecycle, including manufacturing and distribution.
In recent years, the advent of PLM 4.0 marks a transformative shift. This modern iteration embraces cloud-based solutions, predictive analytics, AI, and IoT technologies, providing a true digital thread that ties together all elements of the enterprise. This evolution not only enhances efficiency in data collection and analysis but also accelerates business value by breaking down data silos and enabling informed decision-making.
The historical development of PLM underscores its importance in achieving faster product development cycles, reducing costs, and improving product quality. As industries continue to adopt advanced technologies, PLM remains a critical strategy for maintaining competitiveness in the ever-changing market landscape.
Why Companies Need Product Lifecycle Management
Strategic Resource Allocation: Product lifecycle management (PLM) helps companies make informed decisions about resource allocation. Understanding where each product stands in its lifecycle allows firms to invest wisely in marketing, research, or phase-out strategies. This targeted approach optimizes spending and boosts overall efficiency.
Improved Risk Management: Product lifecycle management enables better risk management. By anticipating market changes and product performance, companies can proactively address challenges before they become critical. This foresight helps maintain market share and brand reputation.
Fostering Innovation: Product lifecycle management fosters innovation. Recognizing when products are approaching maturity or decline prompts companies to develop new offerings or improve existing ones. This continuous innovation cycle keeps businesses relevant and ahead of competitors.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Product lifecycle management enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring products evolve with changing needs and preferences. It allows companies to time product updates or replacements effectively, maintaining customer loyalty.
Streamlined Operations Effective: Product lifecycle management streamlines operations across departments. From design to manufacturing to sales, a unified PLM strategy aligns different teams, reducing miscommunication and improving overall productivity.
In essence, product lifecycle management is not just beneficial—it’s essential for long-term success in today’s dynamic business environment.
The Phases of Product Lifecycle Management
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) encompasses several crucial stages, each focusing on different aspects of a product’s journey from inception to market distribution. Here are the key phases:
Design and Development
This phase is the genesis of the product lifecycle. It includes:
Research: The initial step involves extensive research to understand market needs, customer pain points, and potential opportunities.
Design: Based on the research insights, prototypes are created. Designers leverage tools like CAD software to bring ideas to life.
Development: This step transforms designs into tangible products through iterations and testing. Teams collaborate to ensure the product meets all specifications and standards.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing phase is critical for turning designs into sellable products. Key activities include:
Product Builds: The actual production lines and processes are established to build the product on a large scale.
Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing ensures the product’s quality and consistency. Any defects or discrepancies are rectified before moving forward.
Procurement: This involves sourcing necessary materials and components from suppliers, ensuring they meet quality standards and cost requirements.
Plant Operations: Efficient management of the manufacturing plants, ensuring smooth operation, resource optimization, and maximum productivity.
Distribution
The final phase involves getting the product into the hands of consumers. It includes:
Inventory Control: Managing stock levels to match demand without overproduction or underproduction, minimizing holding costs.
Product Launch Activities: Coordinated efforts to introduce the product to the market, including marketing campaigns, promotions, and public relations.
Logistics: Efficient transportation and distribution channels are critical for timely delivery to various markets.
Supplier Collaboration: Working closely with suppliers to ensure a steady supply chain and to address any potential disruptions promptly.
Understanding these phases is fundamental for effective product lifecycle management, as each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the success and longevity of a product in the market.
Benefits of Product Lifecycle Management
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) offers a wealth of advantages that can substantially enhance an organization’s operations, product quality, and overall efficiency. Understanding these benefits can help companies make informed decisions about integrating PLM into their workflow.
Collaboration
PLM significantly enhances collaboration across various teams and departments. With integrated systems, everyone from engineers to marketers can work from a unified platform. This boosts communication, minimizing misunderstandings and ensuring that everyone is aligned with the project goals. Collaborative planning tools like Creately provide visual workspaces that allow stakeholders to participate in real-time, improving decision-making and project cohesion.
Efficiency
Improved efficiency is another crucial benefit of PLM. By centralizing data and processes, PLM reduces redundant tasks and administrative overhead. This streamlined approach accelerates marketing campaign execution, product development, and other essential activities. For instance, Creately’s data visualization features offer drag-and-drop options from multiple sources, making information easily accessible and actionable.
Quality
PLM fosters higher quality designs and products. The systematic approach to managing product data and processes enables teams to identify and rectify issues early in the development phase. Tools like Creately enable thorough quality assurance processes by providing platforms for collaborative feedback and documentation management. For more insights into process improvement, check out our guide on Quality for Process Improvement.
In summary, the benefits of adopting a PLM strategy are far-reaching. Enhanced collaboration, improved efficiency, and superior product quality are just a few of the advantages. These not only help in faster time to market and reduced errors but also ensure that the final products meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
How to Create a Product Lifecycle Strategy
Developing a robust product lifecycle strategy is crucial for maximizing a product’s potential throughout its lifespan. To begin, clearly define your target market and deeply understand customer needs. This foundation ensures your product addresses real market demands.
Next, craft a distinctive positioning strategy that sets your product apart from competitors. This differentiation will guide marketing efforts and help maintain market share as the product matures.
Assemble a diverse team from various departments to oversee the product’s journey. This cross-functional approach ensures all aspects of the lifecycle are considered, from design to marketing to support.
Establish strong processes for product development, including rigorous design and testing phases. These processes should be flexible enough to accommodate changes based on market feedback.
Implement effective project management techniques to keep development on track and within budget. This helps avoid costly delays and ensures timely market entry.
Throughout the entire process, actively seek and incorporate feedback from customers and key stakeholders. This ongoing dialogue helps the product evolve to meet changing market needs and extends its lifespan.
By following these steps, companies can create a comprehensive strategy that guides their product from conception through growth, maturity, and beyond, maximizing its value at each stage.
How to Measure Product Lifecycles
Understanding and measuring the product life cycle is crucial for optimizing your product development strategies. Here are key metrics and methods to effectively gauge the various stages of a product’s lifecycle:
Sales Data: Track sales performance from product launch to decline. This data helps identify which stage of the lifecycle the product is currently in and forecast future trends.
Customer Data: Collect feedback and analyze user satisfaction levels. This information is vital for making improvements and adaptations in product design and functionality.
Quality of Output: Monitor the quality of products throughout the lifecycle. Quality control metrics are essential for maintaining product standards and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Time-to-Market: Measure the time taken from product ideation to launch. Reducing time-to-market can offer a competitive edge and allow quicker entry into the market.
Cost Efficiency: Analyze the cost incurred at each stage of the product lifecycle, from development to manufacturing and distribution. Cost management is key for maximizing profitability.
Effective metrics and a thorough analysis provide a comprehensive understanding of the product’s performance and areas for improvement. Employing these measurements ensures informed decision-making and strategic adjustments, leading to better resource management and enhanced product success.
Future Trends in PLM
The landscape of product lifecycle management (PLM) is continuously evolving, driven by emerging technologies and new methodologies. Here are some key trends shaping the future of PLM:
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are poised to transform PLM by enhancing data analysis capabilities, optimizing processes, and predicting outcomes. AI can process vast amounts of data to identify patterns, allowing organizations to make informed decisions. Machine learning algorithms can further improve product quality and reliability by identifying potential issues before they become significant problems.
Cloud-based Solutions
The shift to cloud-based PLM solutions is accelerating as companies seek greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Cloud-based PLM eliminates the need for substantial IT infrastructure investments while providing remote access to essential tools and data. This transition enables collaborative efforts across global teams, streamlines updates, and ensures data consistency throughout the product lifecycle.
IoT and Data Analytics
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced data analytics into PLM systems allows for real-time monitoring and management of products. IoT devices can collect data from various stages of the product lifecycle, providing invaluable insights into performance, maintenance needs, and customer usage patterns. This data-driven approach enhances preventive maintenance, reduces downtime, and drives continuous improvement in product design and functionality.
How to Implement Product Lifecycle Management
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) offers a wide range of use cases across various industries, enabling efficient management of the entire product lifecycle. Here are some significant use cases:
Customer-Centricity
PLM plays a crucial role in addressing customer needs effectively. By maintaining a digital thread that integrates feedback from customers, companies can ensure their products meet market demands. This results in improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Time and Cost Estimation
Accurate time and cost estimation are critical for the success of any product. PLM solutions facilitate detailed planning and resource allocation, helping businesses forecast timelines and budgets with precision. Ensuring that projects stay on schedule and within budget limits enhances overall profitability and efficiency.
Change Management
One of the most significant advantages of PLM is its ability to enhance change management processes. By providing centralized data and supporting tools, PLM makes it easier to track changes, evaluate their impact, and implement them efficiently. To learn more about effective change management processes, check out our guide on Change Management
Continuous Improvement
PLM provides a framework for continuous improvement by enabling real-time updates and monitoring throughout the product lifecycle. This results in higher quality products and reduced downtime.
In conclusion, integrating PLM into your business processes can significantly enhance product innovation, reduce costs, and ensure superior product quality, addressing various business needs effectively.
Product lifecycle management (PLM) requires efficient planning, streamlined execution, and continuous collaboration. Creately effectively meets these needs with a suite of powerful features designed to enhance every phase of the product lifecycle.
How Creately Helps in Product Lifecycle Management
Agile Boards
Creately’s agile boards provide an intuitive platform for managing tasks, tracking project progress, and facilitating team collaboration. Agile boards are especially useful for visualizing workflows, ensuring that each stage of the product lifecycle is well-organized and transparent. This feature allows team members to see real-time updates and integrate their contributions seamlessly.
Issue Tracking
Efficient issue tracking is essential in PLM to address disruptions swiftly. Creately offers comprehensive issue tracking capabilities which allow teams to report, monitor, and resolve problems quickly. By using these tracking tools, organizations can maintain high quality and ensure that all product defects are addressed before moving to the next stage.
Product Management Templates
Creately’s extensive library of templates makes it easier to manage different aspects of the product lifecycle. From initial brainstorming sessions to project roadmaps, these templates provide a structured guide that can be customized as per the project requirements. Templates ensure that no critical steps are missed, thereby improving the overall efficiency and quality of the product development process.
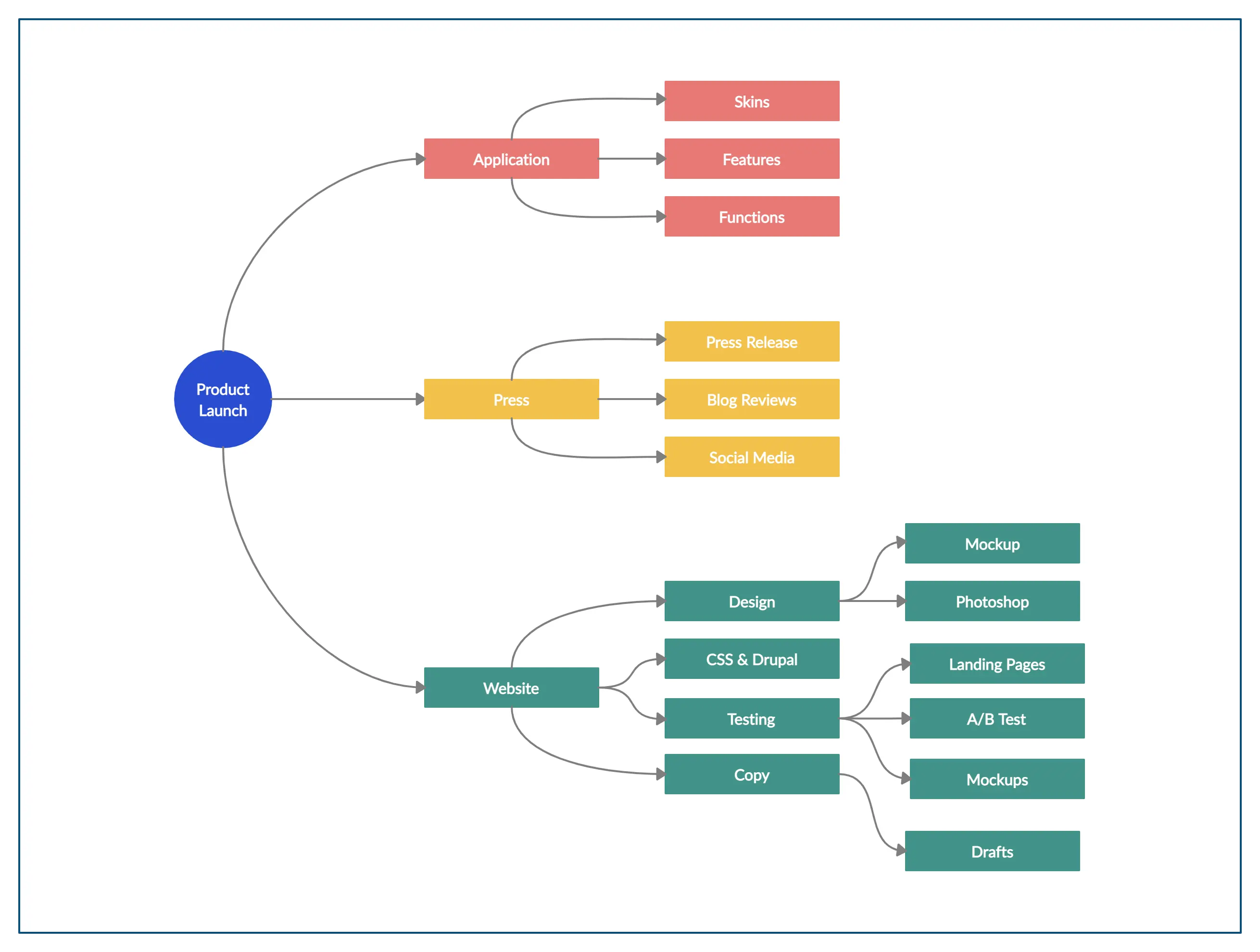
Timelines
Time management is critical in product lifecycle management. Creately’s timeline features enable teams to establish clear deadlines and milestones, facilitating timely completion of tasks. By visualizing the timeline, teams can allocate resources effectively, anticipate potential bottlenecks, and adjust plans as needed to keep the project on track.
Workflows
Creators can design custom workflows within Creately that align with their specific PLM needs. These workflows streamline processes, minimize redundancies, and ensure that each task flows efficiently to the next. The flexibility of custom workflows helps in adapting to the unique requirements of varied projects, enhancing overall productivity.
By leveraging the tools that Creately offers, teams involved in product lifecycle management can experience:
Enhanced collaboration across teams: Creately’s collaborative features allow for real-time communication and information sharing, breaking down silos and fostering a collaborative environment.
Improved efficiency in marketing campaign execution: With templates, timelines, and agile boards, Creately helps in planning and executing marketing strategies more effectively and efficiently.
Streamlined strategy and planning for product development: Customized workflows and issue tracking ensure a smooth transition from one phase of PLM to the next, optimizing strategy and improving project outcomes.
Incorporating these tools within the PLM framework, Creately supports a unified approach to managing product lifecycles, from ideation to market launch.
Embrace the future of PLM with tools that align with modern technological advancements. Explore Creately today to see how it can elevate your product lifecycle management processes and drive your products to success. With its robust capabilities, you can ensure efficient execution and collaboration at every phase, from design to market launch.
FAQs on Product Lifecycle Management
What is a product lifecycle management (PLM) tool?
What are the product lifecycle stages?
The product lifecycle typically consists of five main stages:
-Development: Concept creation, design, and prototyping -Introduction: Initial market launch and customer acquisition -Growth: Increasing sales and market share -Maturity: Peak sales and market saturation -Decline: Decreasing sales and potential product retirement
Understanding these stages helps businesses make informed decisions about product strategy, resource allocation, and innovation efforts.
How does Creately help in product lifecycle management?
Creately supports product lifecycle management through various features:
- Visual collaboration tools for brainstorming and concept development
- Project management features like Kanban boards and Gantt charts
- Customizable templates for product roadmaps and launch plans
- Real-time collaboration capabilities for cross-functional teams
- Integration with other tools to create a seamless workflow
These features help teams streamline their PLM processes, improve communication, and make data-driven decisions throughout the product lifecycle.
What are some effective PLM strategies?
Effective PLM strategies include:
- Implementing a centralized data management system
- Fostering cross-functional collaboration
- Integrating customer feedback throughout the product lifecycle
- Utilizing predictive analytics for informed decision-making
- Adopting agile methodologies for faster iteration and improvement
- Implementing sustainable design and manufacturing practices
- Continuously monitoring and optimizing product performance
- These strategies help organizations maximize product value, reduce time-to-market, and maintain competitive advantage.