Ever wondered how great products—whether it’s your favorite app, a new tech gadget, or even a kitchen appliance—come to life? That’s where product management comes in. It’s the process of guiding a product from idea to launch (and beyond), ensuring it meets customer needs while also driving business success.
Product management sits at the crossroads of business, technology, and user experience. Product managers don’t just come up with ideas; they research, plan, prioritize, and work with different teams to turn those ideas into real products. Whether it’s shaping the next big software tool or improving an everyday product, PMs are the masterminds behind the process.
In this guide we will walk you through what is product management and everything else you need to know about the subject to give you a clear and practical understanding.
What Is Product Management?
Product management is the process of planning, developing, launching, and improving a product to meet customer needs and business goals. It’s about making sure the right product gets built—and that it actually solves problems for the people who use it.
Think of product management as the bridge between business, technology, and user experience. Product managers work closely with teams like engineering, design, marketing, and sales to bring a product to life. They don’t write code or create designs, but they make sure everything is moving in the right direction.
At its core, product management is about understanding what customers need, defining what should be built, and ensuring the product delivers value—both for users and the business. Whether it’s a smartphone app, a new software tool, or a physical product like a smart thermostat, product management is the driving force behind its success.
Great product management can mean the difference between a product that thrives and one that flops. It’s not just about having a good idea—it’s about making that idea work in the real world.
Product Management Process
The product management process is how a product goes from an idea to something real that people can use and love. It’s not just about coming up with ideas—it’s about making sure the right product gets built, launched, and improved over time.
Step 1. Understanding customer needs
Great products start with great insights. Product managers talk to customers, analyze market trends, and gather data to figure out what people truly need. The goal isn’t just to create something new but to solve real problems in a meaningful way.
Step 2. Defining the product vision & strategy
Once the problem is clear, PMs outline a vision—a big-picture idea of what the product should do. They also create a strategy, which is a roadmap for how to build and launch the product successfully.
Step 3. Creating a product roadmap
A roadmap is a plan that shows what features will be built and when. Since no product can do everything at once, PMs prioritize the most important features based on customer needs and business goals.
Step 4. Working with teams to build the product
PMs don’t work alone—they collaborate with designers, engineers, and marketers to bring the product to life. They act as the glue that holds everything together, making sure teams stay focused on what matters most.
Step 5. Testing and refining
Before launching, PMs test the product with real users to catch any issues and gather feedback. This helps fine-tune the product so that it’s useful, easy to use, and enjoyable.
Step 6. Launching the product
A successful launch isn’t just about making the product available—it’s about making sure people know about it and understand its value. PMs work with marketing, sales, and customer support teams to ensure a smooth rollout.
Step 7. Improving and iterating
Once the product is out in the world, the work doesn’t stop. PMs track usage, listen to customer feedback, and continue improving the product over time. The best products evolve based on how people actually use them.
Why Is Product Management Important?
Product management is important because it turns ideas into real products that people actually want and use. It’s the process that makes sure businesses don’t just build things, but build the right things—products that solve real problems, create value, and drive success.
1. It bridges the gap between customers and businesses
Customers know what they want, but they don’t always know how to explain it. Businesses have resources to build products, but they need direction. Product managers act as the bridge, listening to customers, understanding their needs, and translating that into a product that works for both users and the company.
2. It helps companies avoid wasting time and money
Without a clear product strategy, businesses can spend months (or years) building something no one actually wants. Product management helps prioritize what matters, so companies focus on the right features, at the right time, for the right audience.
3. It creates better, more user-friendly products
Great products don’t happen by accident. PMs work with designers and engineers to make sure products are intuitive, useful, and enjoyable to use. Without product management, businesses might launch products that are too complicated, frustrating, or miss the mark entirely.
4. It keeps teams aligned and focused
Developers, designers, marketers, and executives all have different perspectives. Product managers keep everyone on the same page, ensuring that teams are working toward a shared goal rather than pulling in different directions.
5. It drives business growth and innovation
Successful companies don’t just sell products—they create solutions that keep people coming back. Product management plays a key role in continuous improvement, helping businesses adapt, innovate, and stay ahead of competitors.
Product Management Examples
Product management is all about creating and improving products that solve real problems for users while helping businesses grow. It’s a mix of strategy, market research, and teamwork to ensure a product meets customer needs and stands out in the market. Here are some real-world examples of how product management works.
1. Creating a new product based on market needs
Imagine a startup noticing that small businesses struggle with managing invoices. A product manager researches this pain point, talks to business owners, and works with developers to build a simple invoicing tool. Instead of adding complex features, they focus on making the tool easy to use, affordable, and quick to set up. The result? A product that directly addresses a real problem, making it more likely to succeed.
2. Improving an existing product with customer feedback
A video conferencing app finds many users complaining about background noise during meetings. The product team collects feedback, analyzes usage data, and decides to develop an AI-powered noise cancellation feature. By prioritizing what matters most to users, they make the product more valuable, increasing customer satisfaction and retention.
3. Staying ahead of competitors
A food delivery app sees that competitors are offering faster delivery times. Instead of lowering prices or offering discounts, the product team looks at how to optimize delivery routes and improve restaurant partnerships. They introduce a feature that lets users track their delivery in real-time and add an option for priority delivery at an extra cost. This helps them stay competitive while improving the user experience.
4. Expanding into a new market
A fitness app that started with workout tracking notices that many users also want nutrition guidance. The product team researches diet trends and partners with nutritionists to add meal planning and calorie tracking. By expanding the product’s features based on real user behavior, they attract more customers and increase engagement.
Product Management Roles & Responsibilities
A successful product team includes experts from different areas, each playing a key role in turning an idea into a valuable product. Product managers define the vision, while project managers ensure smooth execution by planning, scheduling, managing risks, and keeping teams aligned.
Product manager: Core responsibilities
The product manager is responsible for defining the product vision, prioritizing features, and ensuring the product meets both customer and business needs. A product manager’s role and responsibilities involve:
- Setting the product vision and strategy – Defining what the product aims to achieve and how it aligns with business goals.
- Understanding customer needs – Conducting market research, user interviews, and analyzing feedback to identify real problems.
- Prioritizing product development – Deciding what features or improvements to focus on based on impact and feasibility.
- Coordinating cross-functional teams – Working closely with engineers, designers, marketers, and sales teams to ensure smooth execution.
- Tracking performance and making improvements – Measuring product success through data and iterating based on insights.
Key product team roles
Below we have described the product team structure and product management roles.
1. Product strategy team – Defines the vision and direction
- Chief product officer (CPO) / VP of product – Oversees product strategy, aligns teams with company goals, and mentors product leaders.
- Product manager (PM) – Defines the roadmap, prioritizes features, and ensures alignment with user and business needs.
- Product lead / head of product – Manages multiple product managers and ensures teams stay focused on strategic goals.
2. Project management team – Ensures smooth execution
- Project manager (PjM) – Focuses on how to deliver the product efficiently by managing timelines, risks, and team coordination.
- Scrum master (Agile coach) – Facilitates Agile development, removes roadblocks, and ensures continuous improvement.
3. Product development team – Builds and tests the product
- Product owner (PO) – Manages the product backlog and writes user stories.
- Engineering team (developers, tech leads) – Writes code, develops features, and ensures technical feasibility.
- Technical product manager (TPM) – Bridges communication between product and engineering teams.
- UX/UI designer – Creates intuitive, user-friendly designs based on research.
4. Product marketing & customer experience team – Ensures adoption and satisfaction
- Product marketing manager (PMM) – Creates messaging, go-to-market strategies, and sales enablement content.
- Customer success manager (CSM) – Supports users, collects feedback, and helps improve the product experience.
- Growth product manager (GPM) – Focuses on user acquisition, retention, and monetization strategies.
5. Product operations & support team – Maintains efficiency and user support
- Product operations manager – Optimizes internal workflows and collaboration.
- Support engineers / technical support – Troubleshoots customer issues and improves documentation.
What Is a Product Management Strategy
A product management strategy or product strategy is the plan that guides a product from idea to success. It helps businesses build products that solve real problems, stand out in the market, and continue to improve over time. Without a clear strategy, companies risk creating products that don’t meet customer needs or fail to generate long-term growth.
Understanding customer needs
A great product strategy starts with understanding the customer. Product managers gather insights through market research, customer feedback, and data analysis to identify what people truly need. Instead of guessing, they focus on solving real problems in a way that makes life easier for users.
Defining the product vision
A strong strategy includes a clear product vision—a big-picture idea of what the product should achieve. This vision keeps teams aligned and ensures that every decision supports a common goal. Whether it’s making online shopping easier or helping businesses automate tasks, the vision acts as a guiding force.
Prioritizing what matters
Not every feature or idea can be built at once. A product management strategy helps teams prioritize what to build first based on impact, feasibility, and business goals. The focus is on delivering the most value with the resources available, rather than getting lost in unnecessary details.
Aligning teams and stakeholders
A product strategy isn’t just about the product itself—it also ensures that different teams, from engineering and design to marketing and sales, are working together effectively. Good communication keeps everyone aligned so that the product is built, launched, and supported successfully.
Adapting and improving
Markets change, customer needs evolve, and new technologies emerge. A strong product strategy is flexible, allowing companies to adapt, experiment, and continuously improve their products over time. This ongoing process helps businesses stay competitive and relevant.
Product Management Skills
Product management requires a blend of strategic insight, effective communication, and analytical prowess to guide products from concept to market success. Here are the key skills essential for effective product management:
1. Strategic thinking
- Vision development: Crafting a clear product vision that aligns with company goals.
- Market analysis: Understanding market trends and customer needs to inform product direction.
- Goal setting: Establishing measurable objectives to track product success.
2. Communication and collaboration
- Cross-functional leadership: Coordinating with engineering, design, marketing, and sales teams to ensure cohesive product development.
- Stakeholder engagement: Presenting product plans and updates to executives and other key stakeholders.
- Customer interaction: Gathering and interpreting customer feedback to refine product offerings.
3. Analytical skills
- Data-driven decision-making: Utilizing metrics and analytics to guide product choices.
- Problem-solving: Identifying issues and implementing effective solutions promptly.
- Performance monitoring: Tracking product performance to inform future enhancements.
4. Technical proficiency
- Understanding development processes: Familiarity with software development methodologies to facilitate effective team collaboration.
- Technical communication: Translating complex technical concepts for non-technical stakeholders.
- Feasibility assessment: Evaluating the technical viability of proposed product features.
5. Customer empathy
- User research: Conducting interviews and surveys to gain insights into customer experiences.
- Persona development: Creating detailed profiles to represent key user segments.
- Journey mapping: Visualizing the customer experience to identify customer pain points and opportunities.
6. Adaptability
- Flexibility: Adjusting strategies in response to changing market conditions or feedback.
- Continuous learning: Staying informed about industry trends and emerging technologies.
- Resilience: Maintaining focus and motivation amidst challenges and setbacks.
7. Leadership
- Decision-making: Making informed choices that balance customer needs and business objectives.
- Team motivation: Inspiring and guiding teams towards achieving product goals.
- Conflict resolution: Addressing and mediating disagreements to maintain team harmony.
Product Management Tools
Product managers now have a wide range of tools to streamline their tasks and improve efficiency. These tools support everything from gathering user feedback and tracking progress to collaborating with teams and creating roadmaps. The right tools help manage workflows, enhance communication, and ensure smooth product development.
User behavior tracking
Tools that help understand how users interact with the product, highlighting areas that need improvement. They provide insights into how users behave, helping teams make better decisions.
Feedback and survey tools
These tools collect feedback from users, customers, and stakeholders, guiding product improvements and adjustments.
Collaboration tools
Platforms that enable teams to communicate, share documents, and work together on projects. They make it easier for product managers to stay connected with teams, even when working remotely.
Web conferencing and onboarding
Tools for video calls and presentations. These are used to onboard new users, demonstrate product features, or conduct user testing sessions.
Wireframing and flowchart tools
Tools that help visualize product designs and workflows. They are used to sketch concepts, process mapping, and communicate ideas clearly to teams and stakeholders.
Project management tools
Tools to keep track of tasks, deadlines, and team progress. They help ensure that the product development process stays on track, with everything organized and on schedule.
Roadmap tools
Product roadmap software help product managers create and share product roadmaps. Roadmaps outline product goals, timelines, and milestones, ensuring all teams are aligned.
Product Management Frameworks and Methodologies
In product management, using the right frameworks and methodologies can guide decisions, align teams, and streamline the development process. These tools help product managers tackle complex problems, prioritize effectively, and deliver value efficiently.
Some key frameworks and methodologies to know include:
1. Agile methodology
An agile workflow focuses on iterative development and flexibility. Product teams work in short cycles (called sprints), allowing them to quickly adapt to changes and deliver continuous improvements.
2. Scrum framework
A specific approach to Agile, the Scrum framework divides the work into well-defined roles, events, and artifacts, helping teams stay organized and focused on delivering high-quality products in manageable chunks.
3. Lean product development
Lean focuses on minimizing waste, maximizing customer value, and delivering faster. It encourages building minimal viable products (MVPs), validating ideas with users, and iterating based on feedback.
4. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
OKRs are used to set clear objectives and measure progress toward achieving them. This framework ensures that teams are aligned and working toward common goals.
5. RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort)
RICE is a prioritization framework that helps product managers evaluate ideas based on their potential reach, impact, confidence in success, and the effort required to implement them.
6. Design thinking
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving. It focuses on understanding user needs, ideating, prototyping, and testing solutions to create products that truly resonate with users.
For a deeper dive into 35 essential product management frameworks, check out our guide. It covers these and many more tools to help you optimize your product management approach and build better products.
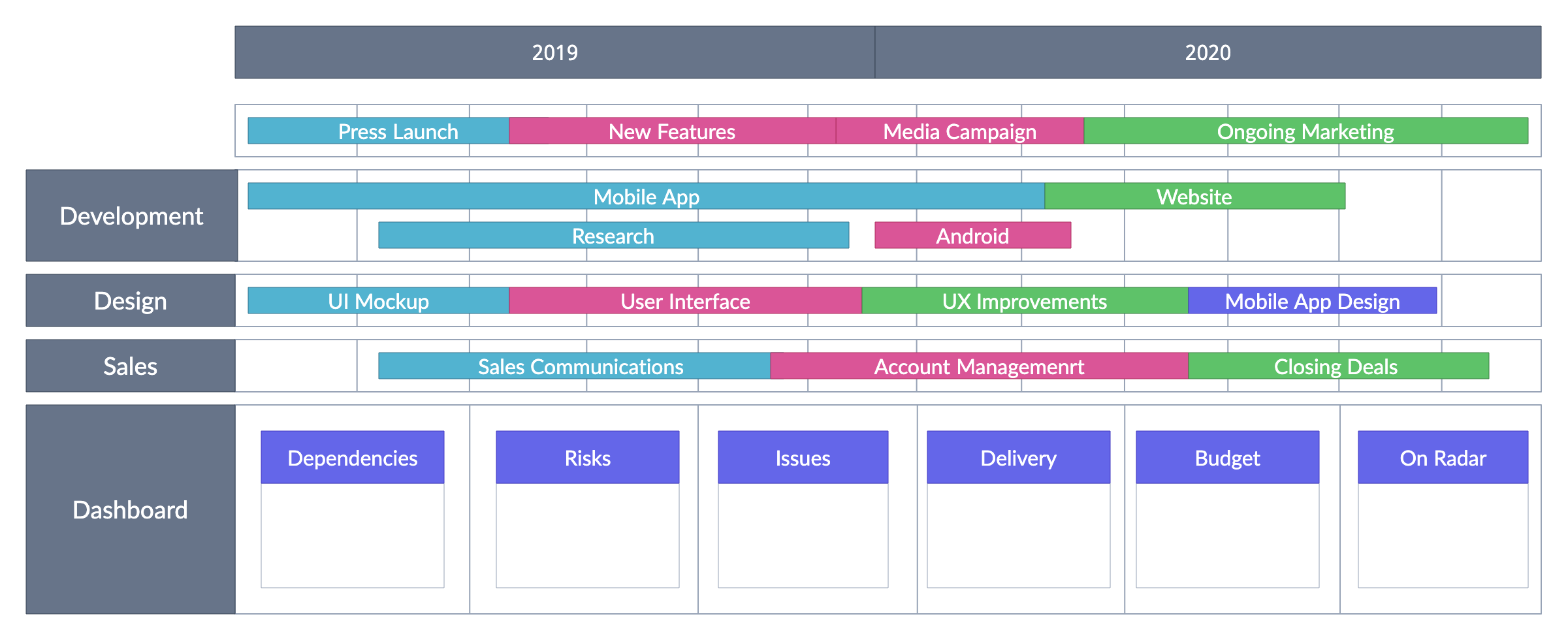
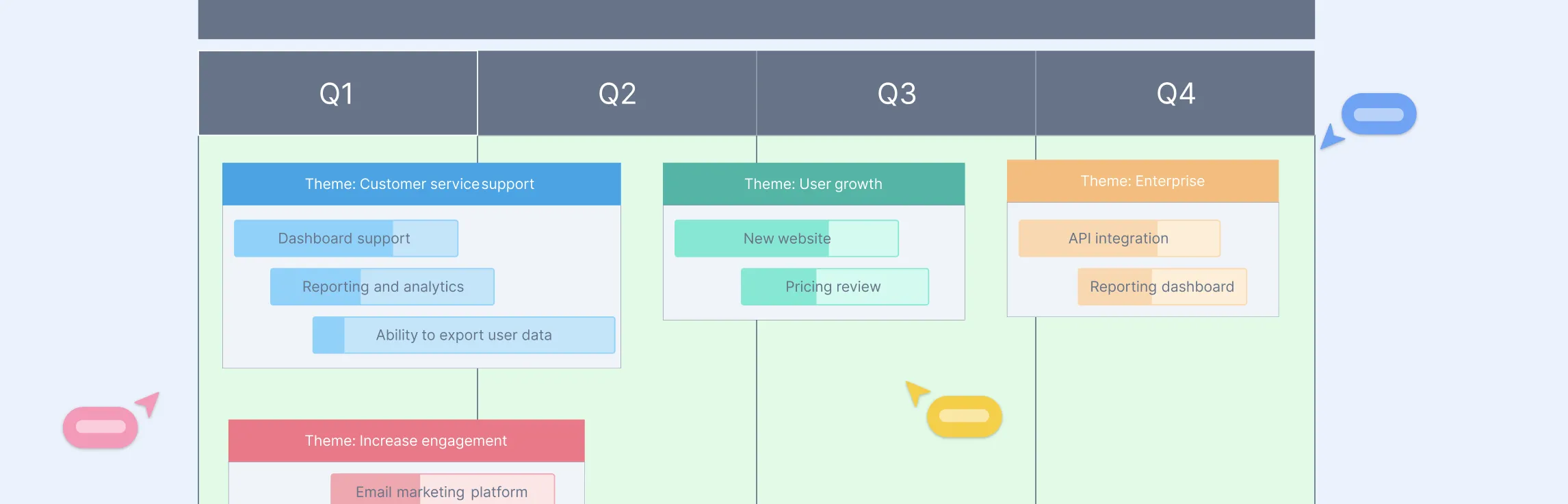
Product Management and Roadmaps
A product roadmap is a strategic tool that outlines the vision, goals, and timeline for a product’s development. It helps product teams stay aligned, prioritize the right tasks, and communicate effectively with stakeholders. Roadmaps are essential for guiding the product through its lifecycle, from ideation to delivery.
Why are roadmaps important in product management?
Roadmaps provide a clear direction for the product, aligning teams with a shared vision and set of goals. They help answer critical questions like:
- What are the product’s main objectives?
- What are the key features and milestones?
- When should we expect delivery, and how do we measure success?
Key components of a product roadmap
- Vision: The overall goal of the product.
- Objectives and goals: Clear, measurable outcomes.
- Timeline: The estimated timeframe for feature releases.
- Milestones: Key phases or checkpoints in product development.
- Features and initiatives: Specific features and product enhancements being developed.
Product roadmaps keep teams on track and provide a clear view of progress, making them an invaluable tool for product managers.
For a detailed guide on how to create a product roadmap, refer to our dedicated article How to Create a Product Roadmap.
What Is Agile Project Management
Agile product management is a flexible, iterative approach to developing and improving products. Unlike traditional product management, which follows a rigid, long-term plan, agile focuses on continuous learning, adapting to changes, and delivering value quickly. It helps teams respond to customer needs faster and create better products through regular feedback and collaboration.
How agile product management works
- Iterative development: Products are built and improved in small steps rather than all at once. This allows teams to test ideas, gather feedback, and make adjustments along the way.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Teams from different areas—such as product, design, and engineering—work closely together to ensure smooth development.
- Customer feedback-driven: Decisions are based on real customer insights, ensuring the product meets user needs.
- Flexible roadmaps: Agile roadmaps focus on goals and priorities rather than fixed deadlines, allowing teams to adapt as needed.
For more detailed insights, check out our full guide on Agile Product Management.
What Is Digital Product Management
Digital product management focuses on building, launching, and improving digital products such as software, apps, and online platforms. Unlike traditional product management, it requires a deep understanding of technology, user experience, and data-driven decision-making.
Digital product managers work closely with engineering, design, and marketing teams to ensure products meet customer needs and business goals. They use agile methodologies, data analytics, and user feedback to continuously refine and enhance digital experiences.
Key aspects of digital product management include:
- User-centered design – Ensuring products are intuitive and valuable to users.
- Data-driven decision-making – Using analytics to track performance and optimize features.
- Scalability and performance – Managing growth, security, and technical challenges.
- Continuous delivery – Releasing updates frequently to improve the product.
For a deeper dive, check out our full guide on Digital Product Management.
B2B vs. B2C Product Management
Product management can look different depending on whether a company is focusing on B2B (Business to Business) or B2C (Business to Consumer) products. While both types of product management share similar principles, there are key differences in their focus, decision-making, and target audiences. Below is a table to help compare the two:
| Aspect | B2B Product Management | B2C Product Management |
| Target Audience | Businesses or organizations | Individual consumers |
| Customer Relationship | Focus on building long-term relationships with clients | Focus on individual users with quick feedback loops |
| Sales Cycle | Longer, often with complex negotiations and decision-making | Shorter, often involving quick, impulse purchases |
| Product Complexity | Often more complex, with multiple features for business needs | Simpler, more intuitive products for everyday use |
| Pricing Model | Custom pricing based on contracts, subscriptions, or volume | Fixed pricing or one-time purchases, often low-cost |
| Marketing Strategy | Targeted, often through account-based marketing and sales | Broad, using digital ads, social media, and brand marketing |
| Feedback Loop | Slower, more formal, gathered from key business stakeholders | Faster, often collected through reviews, surveys, or app analytics |
| Product Development | Focus on solving business problems, often tailored to client needs | Focus on consumer trends, usability, and emotional appeal |
| Team Collaboration | Cross-functional teams (sales, engineering, marketing) | More collaboration with design and marketing for user experience |
| Metrics for Success | Focus on ROI, user retention, and business outcomes | Focus on user engagement, satisfaction, and growth metrics |
Key differences
- Audience: B2B product management involves working closely with business clients, while B2C focuses on attracting and retaining individual consumers.
- Sales and Marketing: B2B strategies often require deeper, more personalized sales and long-term relationships, while B2C focuses on attracting large groups of customers through broad campaigns.
- Product Features: B2B products tend to be more complex, with features tailored to specific business needs, while B2C products are often more straightforward and designed for ease of use.
- Feedback and Iteration: B2B feedback tends to come from a smaller group of key stakeholders and can be slower, while B2C feedback comes from a larger user base and is faster to gather.
Both B2B and B2C product management require a strong understanding of the target market, but the approaches to development, marketing, and customer engagement differ based on the specific needs of businesses or consumers.
Product Management vs Project Management
While both product management and project management are essential roles within an organization, they focus on different aspects of a product’s lifecycle. Understanding the key differences between them can help clarify their responsibilities and how they work together.
Key differences between product management and project management:
- Product Management: Focuses on the entire lifecycle of a product, from ideation to development, launch, and ongoing improvements. Product managers are responsible for setting the vision, strategy, and roadmap for a product, making sure it meets customer needs and business goals.
- Project Management: Focuses on the execution of specific projects within the organization, ensuring that tasks are completed on time, within budget, and according to the project scope. Project managers oversee the planning, execution, and delivery of a project, managing resources and timelines to ensure successful completion.
For a more in-depth explanation and to dive deeper into the differences, check out our detailed guide on Product Management vs Project Management.
Careers in Product Management
A career in product management is both rewarding and challenging. Product managers play a key role in shaping products that impact customers and businesses. They drive the product vision, strategy, and execution, working closely with cross-functional teams to ensure products meet market needs and business goals.
How to a career in product management
- Understand the role: Product management involves defining product vision, collaborating with teams, and making strategic decisions. Familiarize yourself with the key responsibilities and skills needed.
- Develop the right skills: Successful product managers need a mix of technical, business, and communication skills, including problem-solving, market research, and leadership abilities.
- Gain experience: Start by gaining experience in related fields like project management, marketing, or engineering to build your product management expertise.
- Build a portfolio: Work on side projects or internships to demonstrate your ability to manage products and develop strategies.
- Learn continuously: Stay updated through reading, attending conferences, and networking with industry professionals.
- Consider certifications: Certifications in product management, Agile, or project management can enhance your qualifications.
Key career paths in product management
- Product Manager (PM): Entry-level or mid-level, managing product features and aligning products with business goals.
- Senior Product Manager: Manages complex products, shapes product strategy, and mentors junior PMs.
- Product Lead / Group Product Manager: Oversees teams of PMs and ensures alignment with business objectives.
- Product Director / VP of Product: Leads the company’s product strategy and manages teams to drive growth and innovation.
- Chief Product Officer (CPO): Oversees all product strategy across the organization.
History of Product Management
Product management has evolved over time, adapting to changes in business and technology. Here’s a simple look at its history:
Beginnings of Product Management:
- 1930s: Product management began at Procter & Gamble when Neil H. McElroy created the role of “brand manager.” These managers were responsible for guiding a product through its entire lifecycle, from development to marketing, which set the stage for the modern product manager role.
Growth and Expansion:
- 1980s-1990s: Product management grew in the tech industry. Companies like Microsoft introduced program managers who worked to connect engineering teams with business goals, ensuring that products were both technically sound and met market needs.
- 2000s: With the rise of Agile practices, product management became more focused on flexibility and quick adaptation. Product managers started using customer feedback and making changes rapidly to improve products.
Modern Product Management:
- Today, product managers are responsible for creating the product vision, strategy, and roadmap. They work with teams across the company—such as design, engineering, and marketing—to ensure the product succeeds.
- The role is often called the “mini-CEO” of a product, combining business knowledge, leadership skills, and technical understanding. Modern product managers use data and Agile methodologies to quickly adapt to customer needs and market changes.
Product management continues to change as technology and business needs evolve, but it remains a key role for creating successful products.
Streamlining Product Management with Creately
Creately offers a comprehensive suite of features that make product management more efficient, organized, and collaborative. From brainstorming and planning to execution and tracking, Creately’s tools help product managers manage everything seamlessly in one place. Here’s how Creately can transform your product management workflow:
Product management-related templates
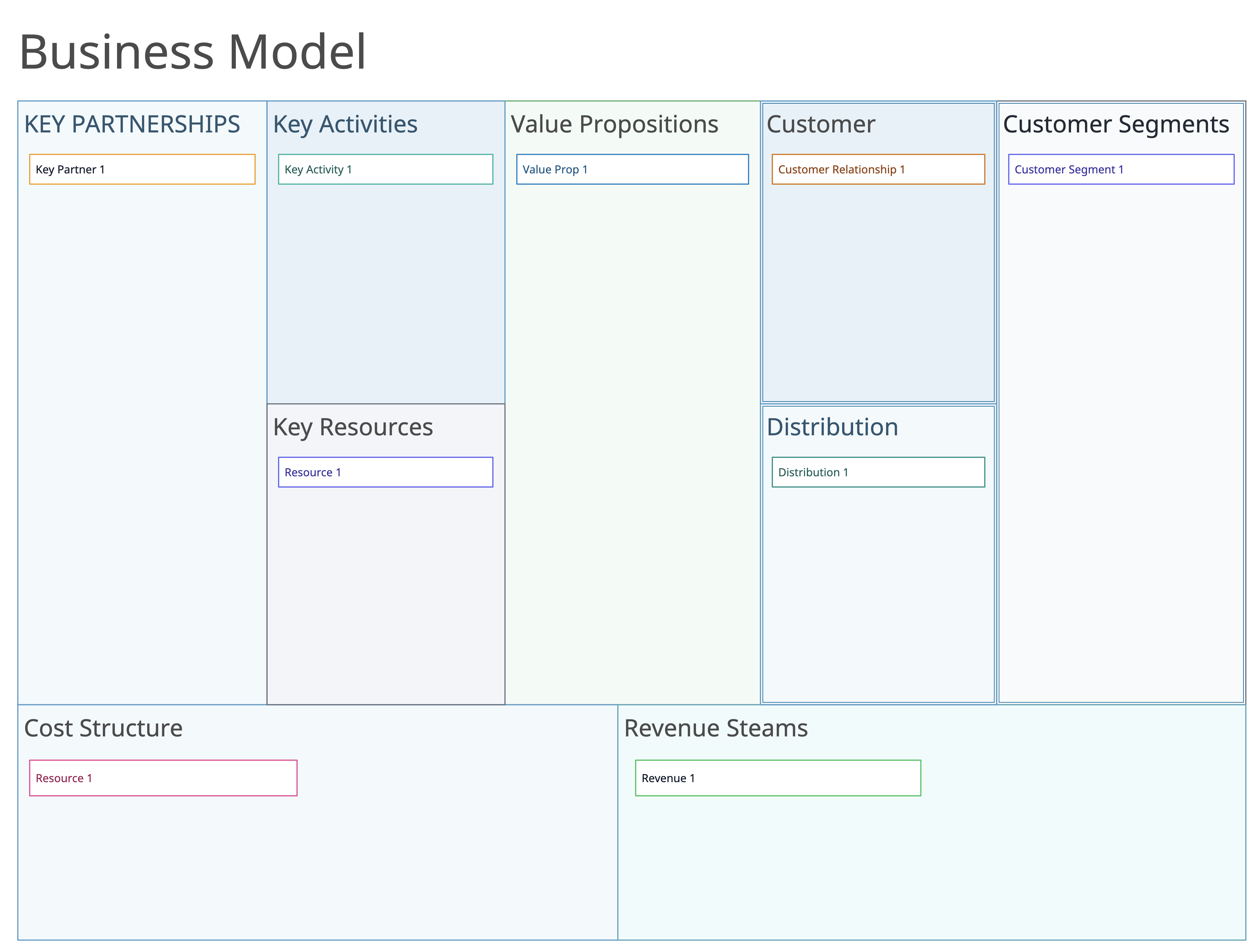
Creately offers a wide range of customizable templates to suit all stages of your product lifecycle, from ideation to execution. These templates cover essential areas such as brainstorming, business modeling, product positioning, customer journey mapping, and prioritization matrices. For instance, you can start with brainstorming templates to gather ideas, then move to the Business Model Canvas to map out your product’s strategy. Creately also includes tools like user personas, SWOT analysis, and roadmaps, helping you visualize your product’s development path and stay aligned with business goals.
Enhanced collaboration sessions
Creately makes it easy for teams to collaborate and stay aligned, no matter where they’re located.
- Voting Sessions: Easily prioritize ideas, features, or tasks through voting sessions. This ensures that your team can focus on the most important items that matter to stakeholders.
- Microsoft Teams Integration: Seamlessly collaborate within Microsoft Teams. This integration helps in sharing, updating, and discussing product management documents in real-time.
- Prioritization Matrices: Use prioritization tools such as RICE, Impact-Effort Matrix, and MoSCoW method to determine the most critical tasks and features in a more visual and efficient way than traditional spreadsheets.
Task management and visual organization
Creately’s task management tools keep you organized and on track throughout the product development lifecycle.
- Kanban Boards: Visualize and manage tasks with Kanban boards. You can easily move tasks through stages and ensure everything stays on track.
- GitHub Integration: The two-way sync feature between Creately and GitHub ensures that changes made in one app reflect in the other. You can manage backlogs, vote on tasks, and change colors of items directly within Creately.
- Jira and Spreadsheet Integration: Creately integrates seamlessly with Jira and spreadsheets, allowing you to manage data from various tools in one place. This gives you a complete, unified view of your tasks and projects.
Efficient Scrum meetings and sprint management
Creately streamlines the Scrum process by helping you visualize tasks, set goals, and track progress with ease. This makes it easier to manage sprints, create backlog items, and run more collaborative Scrum meetings compared to traditional tools like Jira or GitHub.
Collaboration beyond boundaries
Creately’s collaboration features extend throughout the product management process, from initial brainstorming to final product launch. Teams can collaborate efficiently on roadmaps, user stories, and tracking product feedback, all within the same platform, sharing comments and previewing changes in real-time. By simplifying and visualizing tasks, Creately ensures that product managers can keep everyone aligned and focused on delivering a successful product.
Creately VIZ: AI-powered assistance
Creately’s AI tool, Creately VIZ, brings an extra layer of functionality to product management. It can automatically generate diagrams and visuals based on your input, saving time and helping product managers quickly visualize complex ideas and workflows. This AI-powered feature enhances decision-making and collaboration by providing easy-to-understand visuals that everyone can engage with. Whether you’re mapping out a product roadmap or brainstorming features, Creately VIZ helps you create meaningful visuals without needing extensive design expertise.
With Creately VIZ, product managers can instantly generate diagrams including AI flowcharts to streamline their workflow. Here are some useful AI templates for product management:
AI user persona template
AI business model canvas
AI impact effort matrix
Product road mapping capabilities
Creately simplifies product roadmapping by providing customizable templates, drag-and-drop editing, and real-time collaboration features. Product managers can quickly create and update roadmaps to align teams, track progress, and adapt to changes. With multiple roadmap views—such as Gantt charts, Kanban boards, and strategic roadmaps—teams can visualize plans in the way that best suits their workflow. Seamless integration with other tools ensures that roadmaps stay connected to execution.
Helpful Resources
Learn how to create a successful digital product strategy to drive growth and innovation. Explore key steps, frameworks, and best practices.
Explore the different types of product managers and their roles. Learn how each specialization contributes to product success.
Understand the key differences between product management and project management. Learn their unique roles, responsibilities, and how they work together to drive business success.
Discover the key responsibilities of a director of product, their role in product strategy, team leadership, and business growth.
Understand the differences between a product manager and a product owner, their unique roles, responsibilities, and how they collaborate to drive product success.
Conclusion: What Is Product Management
Product management is a vital role that helps create and guide products to meet customer needs and achieve business goals. Over time, the role has changed, from its early days in brand management to the more modern, agile approach we see today.
As companies continue to grow and innovate, product managers are key in leading teams, setting clear goals, and making decisions that impact product success. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to improve your skills, understanding product management’s history, processes, and tools is essential.
By mastering these areas, product managers can lead their teams to create products that stand out in the market and meet customer expectations. The role will continue to evolve, but product managers will always be at the heart of shaping successful products in any industry.
FAQs: What Is Product Management?
How do product managers collaborate with other departments?
What is the difference between product management and product marketing?
What is the product management lifecycle?
How do product managers collaborate with other departments?
What are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in product management?