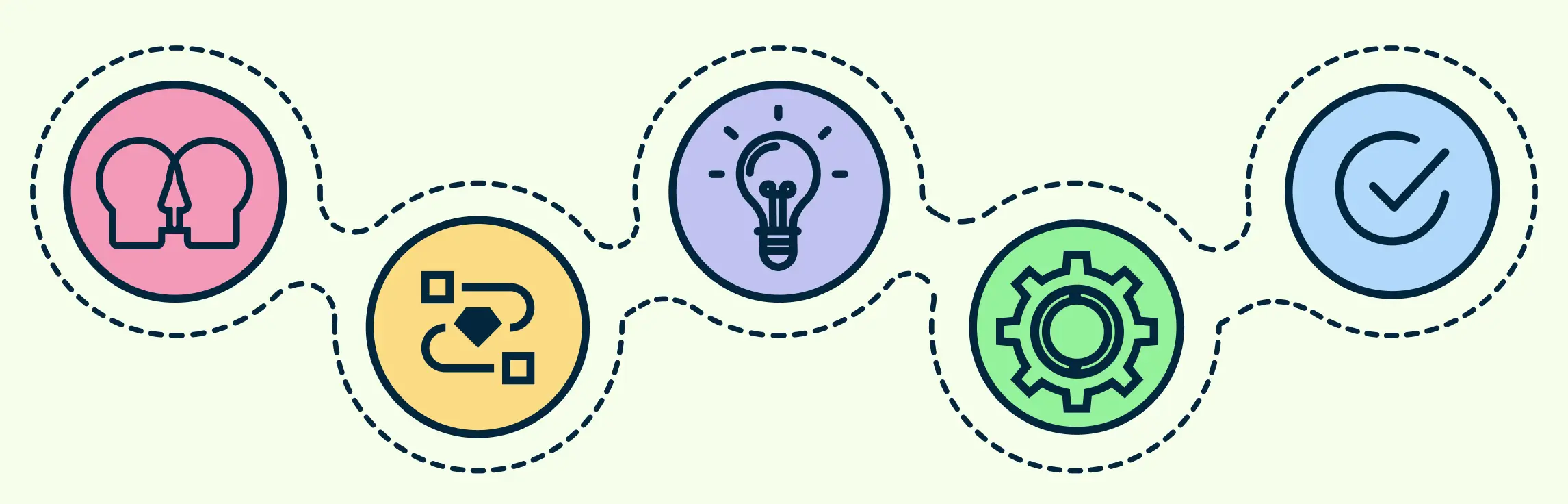
Ever wondered how the world’s most innovative teams consistently solve problems that truly matter? It all starts with the design thinking process—a user-centered, repeatable approach that sparks creativity, uncovers real needs, and leads to solutions that make a difference.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the five essential stages of the design thinking framework, Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test, explaining how each step works and why it’s crucial to meaningful innovation.
Whether you’re building a product, redesigning a service, or solving a complex organizational challenge, this guide is your blueprint for applying design thinking steps with speed, clarity, and purpose.
What Is the Design Thinking Process?
The design thinking process is a structured innovation framework that encourages teams to empathize with users, clearly define the problem, ideate creative solutions, build prototypes, and test them rigorously. These 5 stages of design thinking are not always linear. Teams may loop back and forth between stages as they uncover new insights.
It is a human-centered, iterative method for creative problem solving and developing innovative solutions. Whether you are designing a product, service, or experience, the design thinking approach ensures that the end solution is both desirable and functional. It fosters innovation by systematically combining empathy, creativity, and rationality.
The rise of AI tools for design thinking has made it even more efficient. Teams can now use AI to analyze user feedback, generate prototypes, and even simulate testing scenarios, accelerating every stage of the process.
The 5 Stages of the Design Thinking Process
The design thinking process is typically broken down into five key stages—Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. These design thinking stages form a flexible, non-linear framework that guides teams from identifying user needs to deliver innovative solutions. In the sections that follow, we’ll take a closer look at each stage, breaking down what it involves, how it works, and how you can apply it in real-world scenarios.
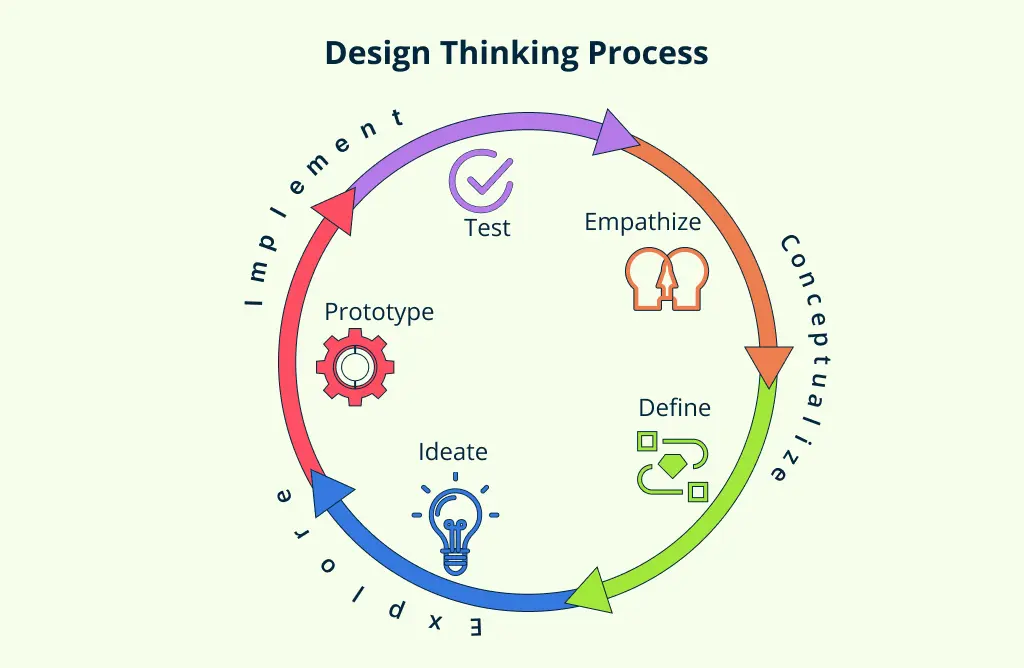
Stage 1. Empathize – Step Into the User’s World
The first stage of the design thinking process is all about developing a deep, human-centered understanding of your users—their needs, challenges, motivations, and emotions. This step lays the foundation for the entire process, as it helps teams connect with users on a personal level before jumping into solutions.
In this phase, it’s crucial to set aside assumptions and approach the problem with a completely non-judgmental mindset. The goal is not just to gather data, but to empathize to see the world through the user’s eyes.
Key Activities:
- User interviews: Conduct one-on-one sessions to uncover detailed user stories and insights.
- Shadowing & immersion: Observe users in their natural environments to understand behaviors and context.
- Field observations: Watch how users interact with existing products, services, or systems.
These qualitative methods help uncover emotional drivers and pain points that numbers alone can’t reveal.
Useful Tools & Diagrams:
- Empathy Maps – Capture what users say, think, feel, and do.
- User Personas – Build fictional characters based on real user data to guide decisions.
- Customer Journey Maps – Visualize the entire user experience across touchpoints.
In the broader design thinking steps, this stage ensures you’re solving the right problem for the right people. Analyzing interview transcripts, identifying emotional cues, and generating empathy maps make this step more scalable. By investing time in empathizing with your users, the design thinking process becomes not just innovative but deeply meaningful and user-first.
Stage 2. Define – Frame the Real Problem
The Define stage is the second step in the design thinking process, where insights gathered during the Empathize phase are analyzed, clustered, and transformed into a clear and actionable problem statement. This stage is about making sense of the chaos, translating user observations into meaningful insights that guide the rest of the journey.
In this critical phase, teams synthesize information to identify core user needs, pain points, and motivations. The aim is to reframe the challenge from the user’s perspective, ensuring that any solutions ideated later are grounded in real problems, not assumptions.
Key Activities:
- Data clustering: Group insights from user research into common themes.
- Insight extraction: Identify key behavioral patterns and unmet needs.
- Problem framing: Craft a clear, user-centered problem statement.
Your problem statement should be human-centered, not solution-focused, and open enough to allow for creative exploration in the next stages. A well-defined problem acts as a guiding compass for all subsequent design thinking steps.
Tools & Diagrams:
- Affinity Diagrams – Cluster research findings to uncover themes.
- 5 Whys Framework – Dig into root causes and core motivations.
- Point-of-View Statements – Frame the user’s problem with empathy and context.
Framing the right problem is half the battle in the design thinking process. With the help of AI, teams can now speed up this step, using NLP tools to automatically tag, categorize, and even summarize user feedback, making synthesis faster and more insightful.
The Define stage ensures your team focuses on solving the most impactful problems. When done right, it unlocks innovation by aligning the team around a common, well-articulated goal rooted in real human needs.
Stage 3. Ideate – Unlock Creative Solutions
The Ideate stage is where imagination takes center stage in the design thinking process. With a clearly defined problem in hand, this phase is all about generating a wide range of creative ideas without judgment or limitations. It’s a space for innovation, where teams are encouraged to think big, explore freely, and consider even the most unconventional solutions.
This stage is essential because it allows teams to move beyond the obvious and dive into unexplored possibilities. By blending diverse perspectives, the design thinking steps in this phase foster original thinking and collaborative problem-solving. Using a real-time collaboration tool such as Creately can be a great way to take this step forward.
Key Activities:
- Brainstorming: Rapid idea generation to explore all possible solutions.
- Role play: Step into the user’s shoes to unlock fresh insights.
- Creative exercises: Use lateral thinking games to fuel imagination.
The Ideate phase thrives when participants feel free to speak up and build on each other’s ideas. This is where quantity breeds quality—more ideas often lead to more refined and effective solutions later on.
Useful Tools & Diagrams:
- Mind Maps – Visualize ideas branching from a central problem or theme.
- Six Thinking Hats – Analyze ideas from six different perspectives: logical, emotional, creative, cautious, optimistic, and managerial.
- SCAMPER Method – Explore ways to Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, or Reverse elements.
- How Might We (HMW) Questions – Reframe insights or problem statements into open-ended questions that encourage solutions, e.g., “How might we help users onboard faster?”
Modern AI tools are supercharging this stage by helping teams generate idea variations, scan competitive landscapes, and even simulate solution outcomes. AI-powered brainstorming assistants can enhance the quantity and diversity of ideas while reducing time spent in workshops.
Ideation is the heartbeat of the design thinking process. It bridges insight and innovation, transforming deeply understood problems into bold, user-focused possibilities.
Stage 4. Prototype – Bring Ideas to Life
The Prototype stage of the design thinking process is where ideas turn into tangible experiences. At this point in the journey, teams take their most promising concepts from the Ideate phase and begin to build quick, low-fidelity models that bring the solution to life. These early versions are not meant to be perfect—they’re tools for learning, exploring, and evolving ideas rapidly.
Prototyping allows teams to visualize ideas, uncover usability issues, and gather real-time feedback before investing in fully developed solutions. This step embraces the mantra: fail fast, learn fast.
Key Activities:
- Build quick mockups based on selected ideas from the Ideate phase
- Simulate user experiences with simple, interactive models
- Identify functionality gaps and usability issues early
Useful Tools & Diagrams:
- UI Mockups – Visual layouts to simulate product interface and user interactions.
- Lean UX Canvas – Aligns teams on assumptions, users, and success metrics.
- Design Thinking Canvas – Maps the entire design thinking process across all stages.
- Storyboards – Visual storytelling tools that illustrate user journeys and interactions.
In the context of the broader design thinking steps, prototyping is a critical bridge between ideas and implementation. It transforms abstract concepts into testable, real-world experiences that bring your vision closer to reality.
Stage 5. Test – Validate and Refine
The Test stage is the final—but not necessarily the last—step in the design thinking process. Here, prototypes are put in front of real users to observe how they interact with the solution, uncover usability issues, and gather honest feedback. This phase is all about validating assumptions, refining solutions, and ensuring the product truly meets user needs.
Rather than seeking perfection, this step encourages continuous learning. Insights gained during testing often lead teams to revisit earlier design thinking steps like ideation or prototyping, reinforcing the process’s iterative nature.
Key Activities:
- User testing sessions: Observe users as they engage with the prototype.
- Feedback collection: Ask targeted questions to uncover what works and what doesn’t.
- Iteration cycles: Make quick changes based on test results and retest.
This phase reveals the real-world usability of the solution. Even small insights—such as where a user hesitates or misunderstands a function—can lead to valuable improvements.
Useful Tools & Diagrams:
- Usability Testing Scripts – Standardized questions and tasks to guide user testing.
- Feedback Grids – Capture what users liked, lacked, and found confusing.
- A/B Testing Tools – Compare multiple design options with measurable outcomes.
- Test Result Dashboards – Visualize user behavior and feedback patterns.
Ultimately, the Test stage ensures that the solution is not only functional but also desirable, feasible, and usable—three cornerstones of the design thinking process. Testing brings the user voice into the final decision-making, making it a vital step toward delivering a successful solution.
Why Use the Design Thinking Process?
The design thinking model is a transformative approach to solving real-world problems by putting people first. Whether you’re developing a new product, improving a service, or streamlining an internal workflow, this human-centered framework helps uncover deep insights and drive meaningful innovation. Here’s why the design thinking process is worth using:
Empathy Leads to Relevance
Unlike traditional problem-solving methods, the design thinking cycle begins with empathy. It encourages teams to truly understand the end user’s needs, behaviors, and pain points, resulting in solutions that are more aligned with what people actually want and need.
Encourages Creative Confidence
The ideation stage of the design thinking cycle promotes open-ended thinking and divergent brainstorming. By separating idea generation from judgment, teams can generate bold, out-of-the-box ideas without fear of failure.
Reduces Risk of Failure
With rapid prototyping and continuous testing, the design thinking process allows you to identify what works and what doesn’t, early in the development cycle. This reduces costly mistakes and ensures you’re building the right solution before scaling.
Fuels Cross-Functional Collaboration
The design thinking process is highly collaborative, involving diverse perspectives from stakeholders, designers, engineers, marketers, and end users. This inclusive approach results in more holistic and viable outcomes.
Adaptable Across Industries
From tech startups and healthcare systems to education and government services, the design thinking process can be adapted to virtually any field where innovation and user experience matter.
In short, the design thinking strategy brings clarity to complex challenges, helping teams move from assumptions to actionable insights—and from abstract ideas to tested, user-validated solutions.
Instantly Visualize the Design Thinking Process with AI
In today’s fast-paced innovation cycles, speed and clarity are key. That’s where AI-powered tools make a real difference. With Creately VIZ, an intelligent diagramming and visual collaboration platform, you can map out each stage of the design thinking process in minutes.
Whether you’re building an empathy map, customer journey map, or Lean UX canvas, Creately’s AI can help you generate, organize, and iterate ideas faster than ever before.
How AI Enhances the Design Thinking Process
- Auto-generate diagrams: Input a short prompt like “5 stages of the design thinking process” and let AI generate a fully editable visual structure.
- Turn ideas into visuals: Quickly convert brainstorming notes into mind maps, prototypes, or customer journey flows with a single click.
- Smart templates: Choose from a library of AI-assisted design thinking templates—from empathy maps to storyboards—to get started instantly.
- Real-time collaboration: Teams can co-create and iterate on diagrams live, with AI offering layout suggestions and formatting improvements on the fly.
By integrating AI into the design thinking process, Creately enables teams to move seamlessly from insight to action, streamlining everything from ideation to testing.
Whether you’re running design sprints, planning user interviews, or presenting to stakeholders, Creately’s AI-powered visual tools ensure that your thinking is not just fast, but beautifully clear and actionable.
How Do Visual Tools Accelerate Design Thinking?
In the fast-paced world of innovation, speed, clarity, and collaboration are essential. That’s where visual tools and digital whiteboards come into play. When integrated into the design thinking process, they turn abstract ideas into tangible, shareable visuals that boost creativity and team alignment—especially during workshops and design sprints.
Clarity Through Diagrams
Complex ideas become easier to understand when visualized. Using tools like empathy maps, journey maps, and system diagrams helps teams gain clarity at every stage of the design thinking process, from defining problems to prototyping solutions.
Faster Alignment Across Teams
Visuals make it easier to align cross-functional teams. Whether you’re in the same room or working remotely, design thinking whiteboards and shared diagrams ensure everyone is on the same page, literally and figuratively.
Creativity Through Visualization
Visual thinking unlocks new ways of problem-solving. When brainstorming is supported by visual collaboration tools, teams can explore connections, patterns, and ideas that might be missed in linear discussions.
Remote Collaboration, Simplified
With distributed teams becoming the norm, digital diagramming tools like Creately make it easy to run virtual workshops. Stakeholders can co-create in real time, leave comments, or instantly generate templates powered by AI.
Visual Tools = Better Design Thinking Outcomes
From sketching wireframes to mapping out user personas, visual tools make the design thinking process more interactive, inclusive, and productive. They not only speed up decision-making but also enhance the quality of collaboration, turning workshops into high-impact, innovation-driven sessions.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While the design thinking process is incredibly powerful, applying it in real-world settings isn’t always smooth. Teams often encounter hurdles that can derail momentum or limit the impact of the process. Understanding these common challenges, and how to overcome them—can help you unlock the full potential of design thinking in your organization.
Resistance to Change
Challenge: mStakeholders and teams may be hesitant to adopt a new, iterative, user-centered approach, especially in environments that favor traditional, linear processes.
Solution: Start small. Use quick wins from design thinking workshops or pilot projects to demonstrate value. Share success stories, bring skeptics into early-stage sessions, and use visual tools to make the process feel more accessible and less abstract.
Ambiguous Problems
Challenge: Sometimes the problem itself isn’t well-defined. Ambiguity in scope, goals, or user needs can stall progress and lead to ineffective solutions.
Solution: Lean into the empathize and define stages. Conduct user research, map insights visually, and collaboratively frame the challenge using “How Might We” questions. Diagrams like journey maps and problem statements help bring clarity to fuzzy or complex problem spaces.
Testing Failures
Challenge: Initial prototypes may fail during testing, which can feel like a setback or be misinterpreted as wasted effort.
Solution: Reframe failure as learning. The design thinking process is built on iteration—fail fast, learn fast. Use testing insights to refine your prototypes and involve users in co-creation. AI-powered diagramming tools like Creately make it easy to update flows and concepts quickly based on feedback.
By anticipating these challenges and applying the right mindset, tools, and collaboration techniques, teams can navigate friction points and stay focused on what matters most—delivering meaningful, human-centered solutions.
Getting Started with Design Thinking in Your Organization
Introducing the design thinking process into your organization doesn’t require a complete overhaul. In fact, the most effective way to embed it is to start small, focus on collaboration, and create momentum through real outcomes. Whether you’re in product development, customer experience, HR, or operations, design thinking can help you drive innovation with purpose.
Start with a Pilot Project
Begin by selecting a real, manageable problem and running a pilot project. This lets your team experience the process end-to-end without major risk or disruption. Choose a challenge that’s visible and impactful to quickly demonstrate the value of design thinking.
Build Cross-Functional Teams
The design thinking process thrives on diversity of thought. Bring together cross-functional teams with different perspectives, designers, developers, marketers, customer service, and even end users. This encourages co-creation and leads to more holistic solutions.
Embrace Rapid Iteration
Don’t wait for perfection. Encourage a mindset of rapid iteration, build low-fidelity prototypes, test quickly, gather feedback, and refine. This speeds up learning and increases the chances of finding what truly works for your users.
Use the Right Tools
Equip your team with tools that support visual collaboration and flexibility. Platforms like Creately make it easy to map out ideas, document insights, and work visually, whether you’re in the same room or across time zones.
By fostering a culture of experimentation, empathy, and co-creation, your organization can move from rigid problem-solving approaches to a more agile, innovative mindset powered by the design thinking process. It all starts with one project, one team, and a willingness to think differently.
Turning Insights into Innovation with the Design Thinking Process
The design thinking process is more than a method, it’s a mindset that puts people first and fosters meaningful innovation. By understanding and applying its five core stages, Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test, you can consistently create solutions that are not only effective but also deeply user-focused.
With the power of AI and smart visual tools like Creately, you can bring these stages to life faster, better, and more collaboratively. From generating empathy maps to prototyping UI mockups, AI takes the manual work out of the equation so your team can focus on creativity and problem-solving.
Whether you’re starting from scratch or refining your design workflow, this guide equips you with everything you need to confidently apply the design thinking process, and scale innovation through visual clarity and AI-powered efficiency.
FAQs About the Design Thinking Process
What industries can benefit from the design thinking process?
How long does the design thinking process typically take?
How is the design thinking process different from traditional problem-solving?
Can the design thinking process be used by individuals, or is it only for teams?
What Are the 5 Core Design Principles?
Can I Generate the Design Thinking Process with AI?
Resources:
Razzouk, R. and Shute, V. (2012). What Is Design Thinking and Why Is It Important? Review of Educational Research, [online] 82(3), pp.330–348. doi:https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654312457429.
Waidelich, L., Richter, A., Kolmel, B. and Bulander, R. (2018). Design Thinking Process Model Review. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC). [online] doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/ice.2018.8436281.