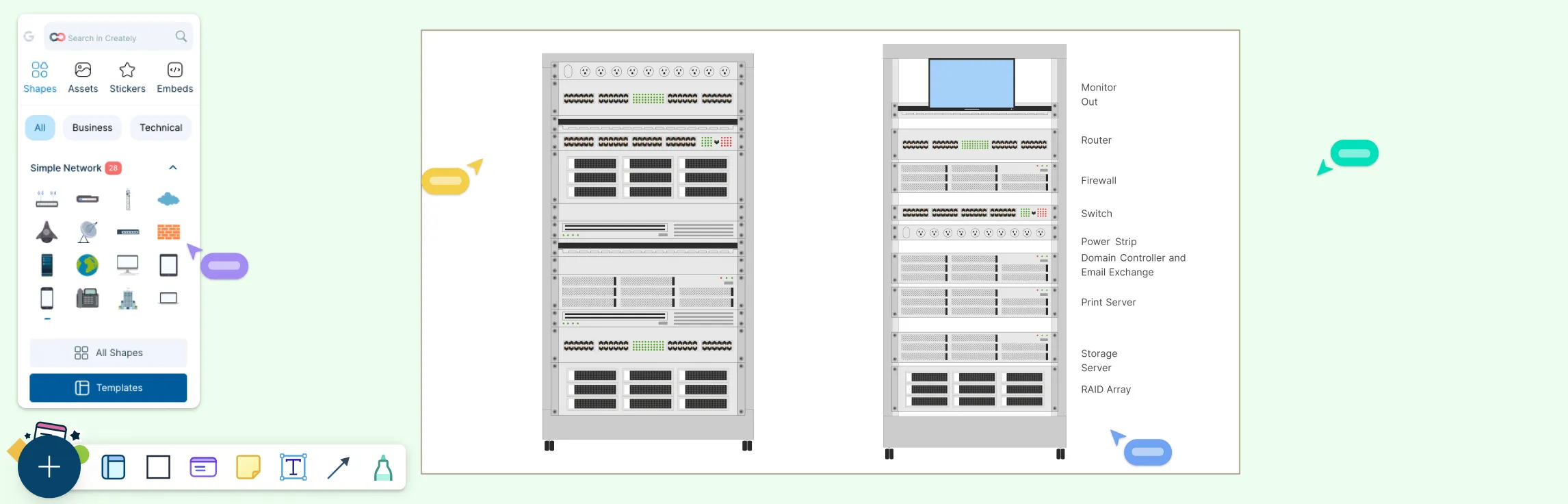
Visualizing your network’s security setup is key to keeping systems safe and organized. Firewall network diagrams help IT teams see how traffic flows, identify weak points, and plan robust defenses. In this guide, we’ll explore practical examples and templates you can use to design clear, effective firewall diagrams for any network.
What Is a Firewall in Computer Network
A firewall is like a security guard for your network. It monitors all the traffic coming in and going out, letting safe data through and blocking anything suspicious. Whether it’s stopping hackers, preventing malware, or keeping sensitive info safe, firewalls are your first line of defense. They can be physical devices, software programs, or even virtual cloud solutions — whatever your setup, a firewall keeps your network secure and under control.
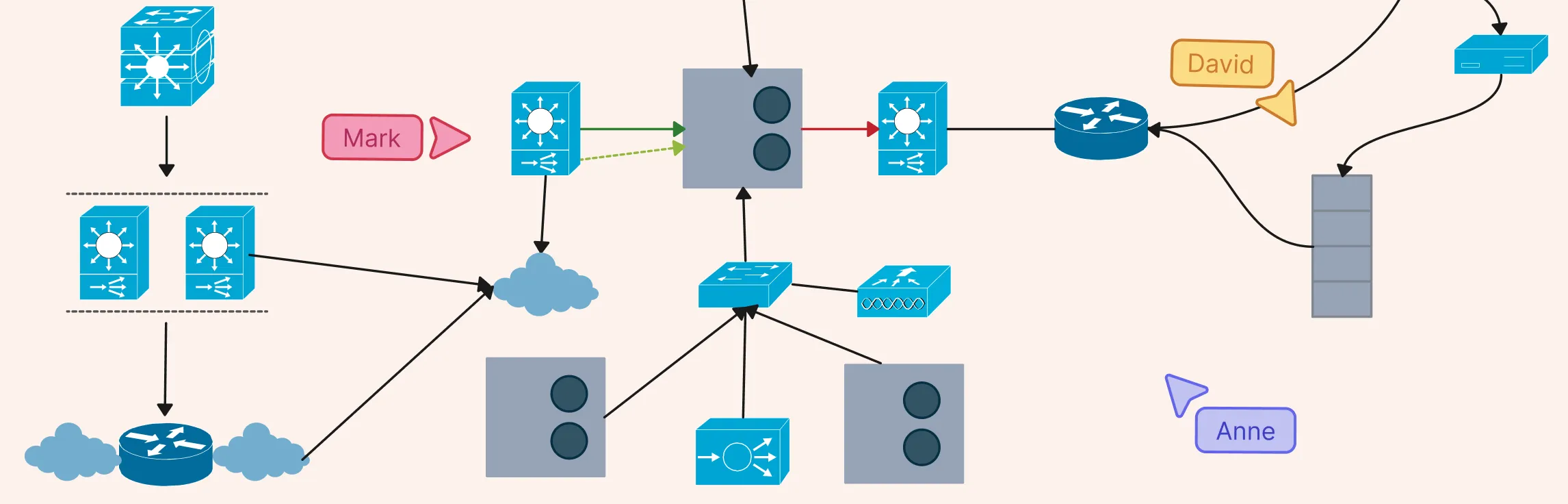
A firewall network diagram is a visual map that shows where firewalls sit in your network and how traffic flows between trusted and untrusted zones. It helps teams quickly understand, plan, and secure their network.
A firewall diagrams show:
Firewall placement – where firewalls sit in your network.
Traffic flow – how data moves between zones.
Trust boundaries – where inspection points and security rules apply.
Free Editable Firewall Network Diagram Templates
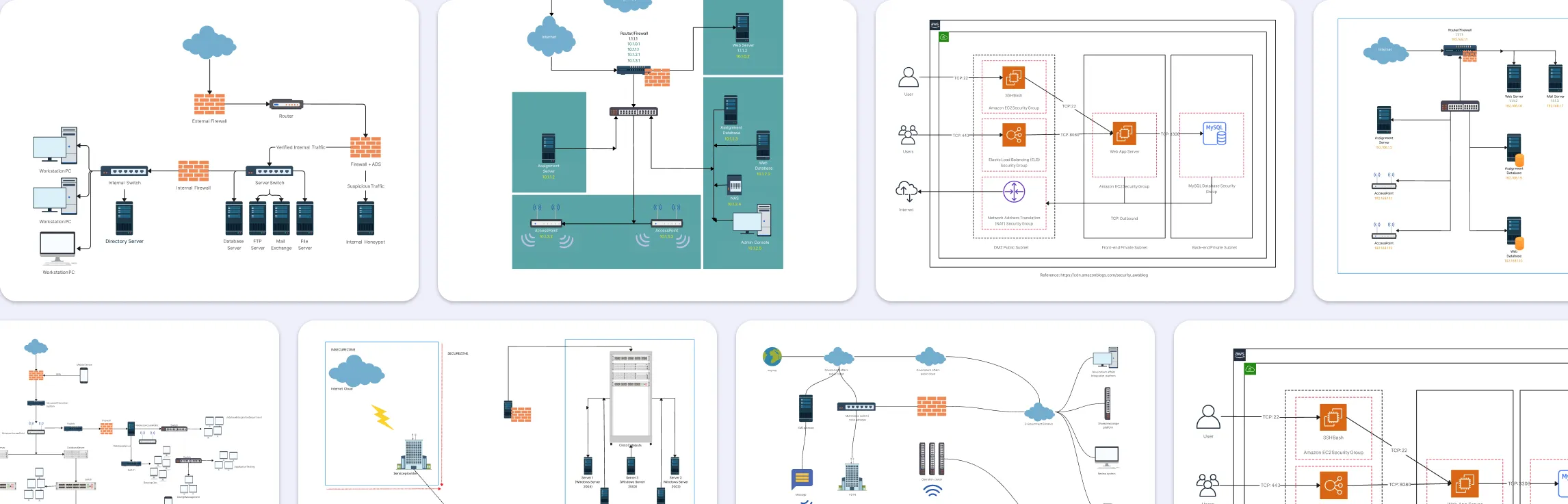
Below are practical, real-world firewall network diagram examples you can reference or adapt for your own network documentation:
1. Internet Firewall Deployment
Shows how an internet-facing firewall protects internal resources and controls traffic between the internet, public services (DMZ), and your internal network. This type of diagram makes it clear where perimeter defenses are placed.
2. Distributed Firewall Topology
Illustrates a network with firewalls placed at multiple points, not just at the perimeter. Distributed firewall setups are common in larger enterprises where segmented traffic control improves security and reduces lateral movement.
3. UTM Firewall Diagram
Visualizes a unified threat management (UTM) firewall that combines multiple security functions (like filtering, antivirus, and intrusion prevention) into one device. This helps teams see how layered security tools integrate into network flow.
4. Firewall Zone Diagram
Focuses on visualizing different network zones (such as internal, external, and DMZ) and how firewalls enforce boundaries between them. It’s great for showing trust levels and controlled traffic paths.
5. Simple Network Firewall Diagram
A simple, clean network layout that can be adapted to include firewall icons and zones. It’s useful when you want a foundational view before adding security layers.
6. Basic Firewall Network Diagram
General network structure diagrams without firewalls can also serve as a starting point. You can build on them by marking firewall positions and security segments.
7. CAD Network and Firewalls
Diagrams that merge architectural network views (CAD style) with firewall placements offer detailed layouts useful in physical infrastructure planning.
8. IIIT Firewall
Tailored examples like institutional network firewall diagrams provide context for environments with specific access control needs (e.g., campus networks).
Why Use Creately for Firewall Network Diagrams
Creately’s network diagram software helps you quickly design and document firewall network setups using ready-made templates and simple visual tools. Instead of starting from scratch, you can adapt proven layouts to match your real network.
1. Ready-made templates
Get started fast with firewall network diagram templates for common setups like perimeter firewalls, DMZs, and zone-based architectures.
2. Quick and easy editing
The quick access toolbar appears at the top of each shape, giving you instant access to colors, text, and connectors—making it easy to highlight zones and critical firewalls.
3. Clear zones and traffic flow
Use containers, colors, and arrows to clearly separate internal networks, external networks, DMZs, and cloud segments, and show how traffic moves between them.
4. Context, collaboration, and sharing
Add notes and attachments for firewall rules, collaborate in real time with your team, and use presentation mode or exports to share diagrams for reviews, audits, or training.
FAQs About Network Diagrams with Firewalls
How are firewalls deployed?
What are security zones?
What are the common types of firewalls?
Why use multiple layers of firewalls?
What symbols are used in firewall network diagrams?
How to create an effective network diagram with firewall?