When you’re working with complex family histories, scattered case notes and long, tangled stories can make it nearly impossible to see the bigger picture. Therapists often feel the frustration firsthand, trying to track emotional legacies, repeating roles, and intergenerational trauma without a clear visual map. Transgenerational Therapy offers a powerful way to understand how patterns move across generations, and when paired with tools like genograms, the work becomes even clearer and more actionable. This guide walks you through the core concepts, models, and patterns behind this approach, plus how modern tools make it easier to support your clients with clarity and confidence.
What Is Transgenerational Theory?
Transgenerational theory explains how emotional legacies, belief systems, roles, and unresolved conflicts are passed down from one generation to the next, often without families realizing it. Instead of viewing family issues as isolated events, this approach looks at the bigger story: the patterns that began long before the current generation. Therapists use this framework to understand why certain behaviors keep repeating and how deeply rooted dynamics shape present-day relationships, coping strategies, and emotional responses.
What Is Transgenerational Therapy?
Transgenerational therapy is a family therapy approach that helps individuals and couples understand how emotional patterns, beliefs, trauma, and relationship roles are passed down through multiple generations. Instead of focusing only on the “here and now,” it looks at the bigger picture, how unresolved conflicts from parents, grandparents, and even earlier ancestors continue to shape current behavior, communication styles, and relational struggles. This clearer, broader perspective creates space for healing patterns that might otherwise remain invisible.
As part of broader transgenerational models of family therapy, this approach combines emotional insight, family systems thinking, and multigenerational exploration. Therapists use it to identify inherited patterns, make sense of recurring relationship issues, and help clients build healthier ways of relating. Where transgenerational theory explains why patterns repeat, transgenerational therapy gives clients tools and interventions to change those patterns in real time.
Although often compared to other family therapy models, such as structural, strategic, or solution-focused therapy, transgenerational therapy stands out in a few key ways:
- Structural therapy focuses on present-day boundaries and hierarchies.
- Strategic therapy zooms in on immediate problem-solving.
- Bowenian therapy shares similarities, but emphasizes differentiation and emotional distance more explicitly.
Transgenerational Therapy, in contrast, blends emotional history with real-world behavior. It’s about uncovering the lineage of a problem rather than just addressing the symptoms.
Because these patterns often span decades, therapists rely heavily on visual thinking tools, especially genograms. Mapping relationships visually helps them spot cycles earlier, organize complex histories effortlessly, and see connections that would be easy to miss in scattered notes or long narratives. Visual mapping transforms overwhelming stories into clean, interpretable insights, making it easier to guide families toward meaningful change.
What Can Transgenerational Family Therapy Help With?
Transgenerational Family Therapy is designed to address a wide range of emotional, relational, and behavioral challenges that often have roots in multiple generations. By uncovering patterns and emotional legacies, it helps families and individuals gain clarity, break negative cycles, and build healthier relationships.
Some of the key areas it can support include:
- Breaking repeating family patterns: Identify inherited behaviors, communication styles, and role expectations that affect current relationships.
- Healing intergenerational trauma: Address unresolved grief, abuse, or conflict that may be impacting multiple family members.
- Improving couple and parenting dynamics: Recognize how parental or relational patterns influence current interactions and attachment styles.
- Clarifying emotional roles and boundaries: Understand inherited roles like scapegoat, family hero, or caretaker and learn healthier ways to relate.
- Enhancing self-awareness and resilience: Support individuals in differentiating themselves while maintaining strong family connections.
By combining these insights with visual tools like genograms, therapists can guide families to actionable understanding and meaningful change.
What Is Transgenerational Trauma
Transgenerational trauma refers to the ways traumatic experiences, unresolved conflicts, or destructive patterns can be passed down from one generation to the next, often without family members even realizing it. Unlike isolated events, these traumas persist over time, subtly shaping beliefs, behaviors, emotional responses, and relationships within the family system.
A transgenerational problem or issue can appear in many forms, including:
- Recurring family conflicts and unresolved disputes
- Patterns of verbal, emotional, or physical violence
- Challenges with mental health, addiction, or emotional regulation
- Trauma tied to major life events affecting multiple generations, such as war, economic hardship, loss, or family-specific tragedies
Recognizing these patterns is the first step toward healing. By exploring the origins of transgenerational trauma and mapping its effects across generations, therapists and clients gain clarity about how past experiences influence present behavior. This understanding is critical for promoting emotional health, breaking negative cycles, and fostering stronger, more harmonious family relationships.
Visual tools like genograms and family trees are particularly useful here, helping therapists trace inherited patterns, connect events to emotional outcomes, and design interventions that address both past and present dynamics.
7 Core Principles of Transgenerational Family Therapy
At its core, transgenerational family therapy is built on several guiding principles that help make sense of these inherited patterns:
1. Intergenerational Transmission
Families don’t begin with the people in the therapy room. Ideas, fears, expectations, and emotional reactions often echo from earlier generations. Transgenerational theory focuses on identifying these echoes, seeing how past experiences subtly (or not so subtly) shape current behavior.
2. A Family Systems Lens
Instead of viewing individuals in isolation, the theory treats the family as an interconnected system. Every member’s actions affect the whole. This systemic viewpoint helps therapists identify how certain interactions or alliances maintain long-standing patterns.
3. A Multigenerational Perspective
Therapists look beyond the immediate family to uncover how roles, loyalties, and conflicts evolve across multiple generations. This panoramic approach reveals deeper roots of present-day challenges that might otherwise go unnoticed.
4. Unconscious Processes
Not all family dynamics are visible or openly discussed. Many patterns operate under the surface; unspoken rules, inherited fears, emotional cutoffs, or protective behaviors. Transgenerational theory helps bring these hidden influences into conscious awareness so families can work through them thoughtfully.
5. Differentiation of Self
A key goal in this model is helping individuals maintain their own identity while staying emotionally connected to the family. Higher differentiation leads to healthier boundaries, greater resilience, and less reactivity within generational patterns.
6. Family Strengths and Resilience
Transgenerational work isn’t only about uncovering trauma; it’s also about highlighting the strengths, survival strategies, and values passed through generations. Understanding these strengths helps families build healthier relational patterns moving forward.
7. Narrative Exploration
Families carry stories about who they are, what they’ve survived, who plays what role, and what “should” or “shouldn’t” happen. Transgenerational therapy encourages families to examine and rewrite these narratives in more empowering ways.
Key Transgenerational Patterns Therapists Look For
In transgenerational patterns family therapy, certain recurring dynamics often emerge across generations, helping therapists understand why families repeat the same struggles or conflicts. By identifying these patterns, therapists can guide families toward healthier interactions and break long-standing cycles.
Alliance Shifts, Cutoffs, and Enmeshment
Families often form shifting alliances or experience cutoffs, where emotional connections are abruptly severed. Enmeshment, where boundaries between family members are blurred, can leave individuals unable to differentiate themselves. Mapping these patterns visually makes it easier to see which relationships are influencing current behaviors.
Multigenerational Trauma Patterns
Trauma isn’t always confined to the individual who experienced it first. Unresolved grief, abuse, or neglect can ripple across generations, shaping behaviors, coping strategies, and emotional reactions. Therapists use visual tools like genograms to trace how trauma moves through the family system.
Role Inheritance
Certain roles; like the scapegoat, the family hero, or parentified children, often repeat in different generations. These roles can shape identity and limit personal growth unless they are recognized and addressed. Visual mapping helps highlight these inherited roles and their impact.
Patterns Visible Only Through Visual Mapping
Some dynamics are subtle or unconscious and may go unnoticed in conversation alone. Using genograms, therapists can reveal cycles of conflict, loyalty, or avoidance that are otherwise invisible, making intervention more precise and effective.
By understanding these transgenerational patterns, therapists can connect past family histories to present-day struggles, offering insight, clarity, and actionable steps for change.
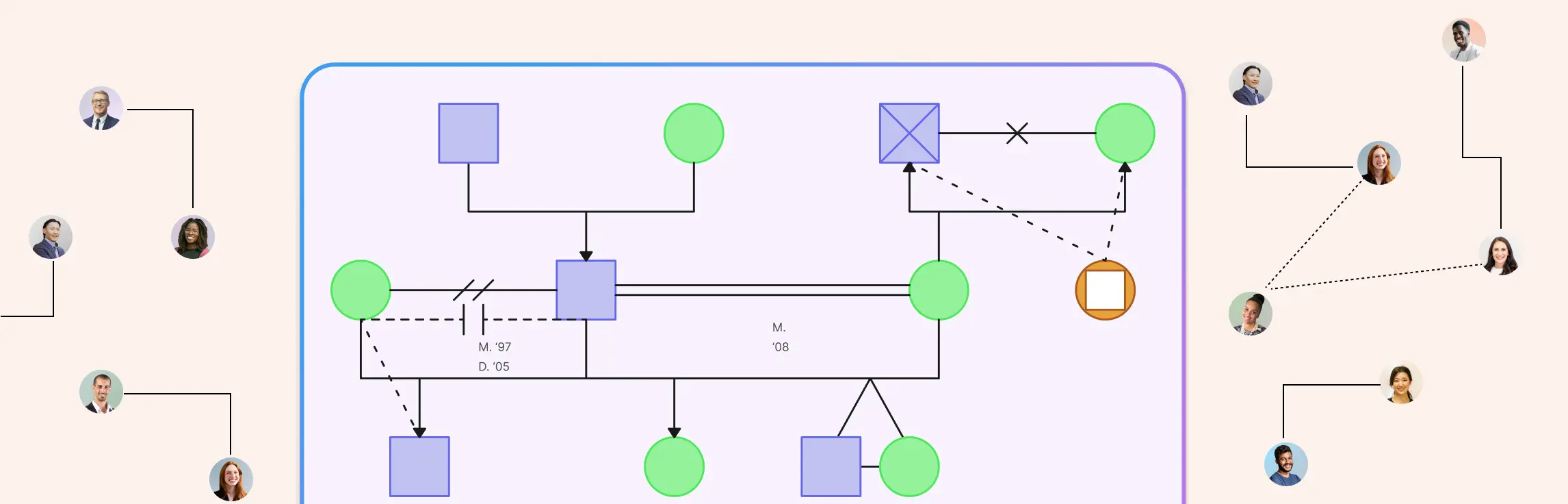
How Genograms Transform Transgenerational Therapy + Free Templates
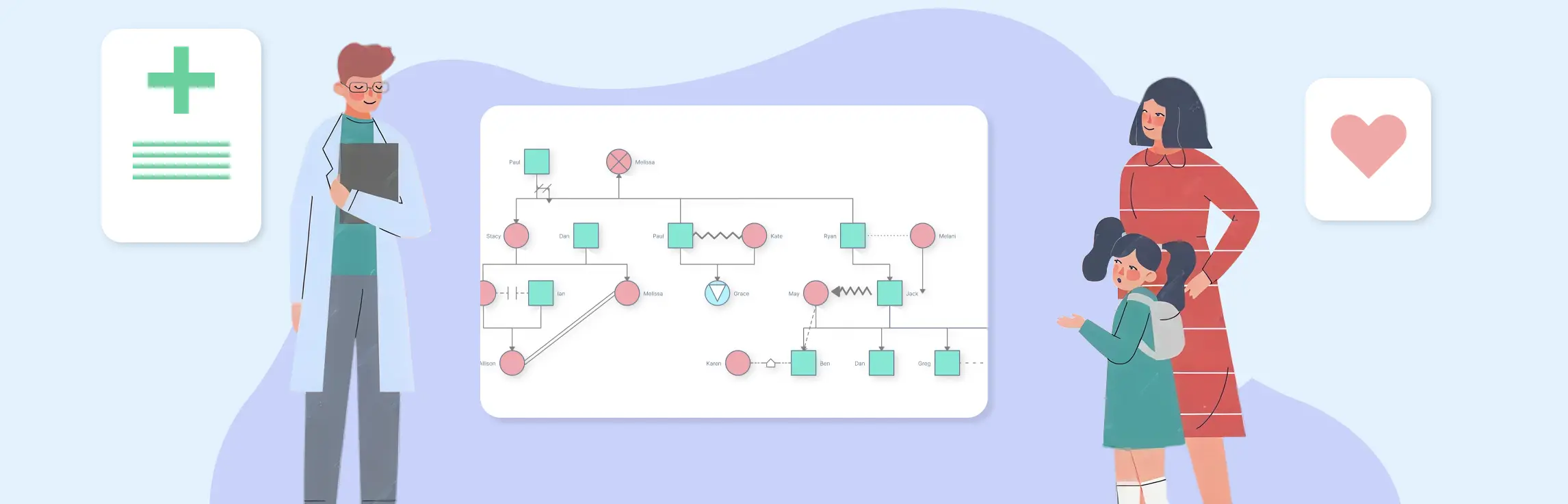
Genograms are one of the most important tools in transgenerational therapy because they make the invisible visible. Instead of relying on long stories, scattered session notes, or clients’ fragmented memories, a genogram turns an entire family history into a clear, structured map that therapists can work with confidently.
Why Genograms Matter in Transgenerational Work
When you’re exploring patterns that go back three or four generations, it’s almost impossible to hold everything in your head. Genograms help therapists:
- track emotional legacies and roles across time,
- identify repeating patterns like trauma cycles or cutoffs,
- visualize how major life events shape the family system,
- and quickly spot contradictions, gaps, or hidden dynamics that might not surface in conversation.
This is why many clinicians prefer working with a dedicated therapy genogram software instead of sketching by hand. Digital visual mapping makes it easier to update information, experiment with hypotheses, and layer in emotional or relational data without losing clarity.
Why Creately Works Well for Transgenerational Therapists
Creately gives therapists a simple, visual space where family information becomes organized and actionable. You can start with ready-made genogram templates, add symbols with one click, and build a multigenerational map that stays clean no matter how complex the family story is.
It reduces cognitive load, saves time during and between sessions, and helps therapists move from “lots of information” to “clear insights” much faster.
Here’s why Creately stands out for transgenerational therapy work:
- Smart Child Connector Bar: Easily add and connect multiple children at once, with lines that adjust automatically to keep diagrams neat and organized.
- Automatic Cultural Genograms: Visualize cultural heritage and blended family structures effortlessly. Parental colors flow to children, making it simple to represent multicultural families.
- Comprehensive Genogram Shape Library: Access the largest collection of genogram-specific shapes for gender, identity, medical conditions, and more.
- Support for All Family Relationships: Map marriages, divorces, adoptions, and emotional bonds with built-in connectors for every type of relationship.
- Customizable Genogram Templates: Jumpstart projects with ready-to-use templates designed for clinical, educational, cultural, or personal use cases.
- Freeform Infinite Canvas: Work without limits on a zoomable canvas that allows mapping of complex family structures, adding layers of context, and connecting insights in one view.
With Creately, therapists save time, reduce cognitive load, and move from “too much information” to clear, visual insights, making multigenerational therapy faster, simpler, and more effective.
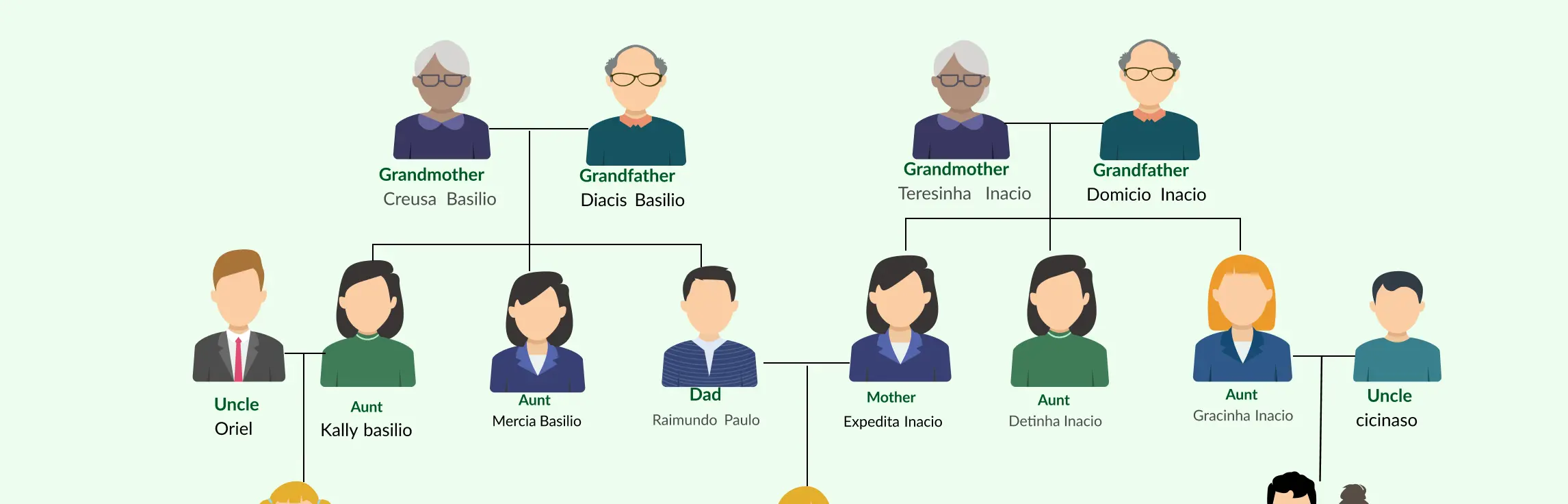
Explore Family Trees for Personal Insights
For individuals or families curious about their ancestry, cultural roots, or personal history, family trees are another powerful tool alongside genograms. Creately makes it easy to build detailed, visually appealing family trees that highlight connections, heritage, and lineage without the complexity of clinical symbols.
With Creately, users can:
- Create multi-generational family trees quickly using family tree templates
- Add images, dates, and notes for each family member
- Explore cultural backgrounds and blended family structures visually
- Zoom, expand, and reorganize the tree freely on the infinite canvas
- Share or collaborate with relatives to enrich the family story
Whether you’re a therapist mapping emotional legacies or a personal user exploring ancestry, Creately combines the power of genograms and family trees to make complex family information clear, organized, and engaging.
Transgenerational Therapy Techniques Explained
Transgenerational therapy techniques are the practical tools therapists use to interrupt inherited cycles and help families build healthier relational patterns. Rather than simply identifying what’s been passed down, these techniques focus on what to do once those patterns become visible. They bring structure, clarity, and direction to the therapeutic process, making deep multigenerational work more actionable.
1. Assessment Through Multigenerational Exploration
Therapists begin by gathering stories, histories, and emotional themes across at least three generations. This isn’t just casual conversation, it’s a structured assessment method that uncovers how beliefs, coping mechanisms, and communication styles formed over time. This foundation guides all transgenerational therapy interventions that follow.
2. Insight-Based Interventions
Once patterns are identified, therapists use guided reflection techniques to help clients understand why these patterns exist and how they influence present behaviors. This may include exploring emotional legacies, repeating marriage dynamics, intergenerational trauma responses, or inherited conflicts. The goal is to generate insight that leads to conscious choice instead of automatic repetition.
3. Boundary and Differentiation Work
A core component of transgenerational therapy techniques is strengthening a client’s ability to maintain a clear sense of self within the family system. Therapists help individuals or couples practice emotional boundaries, reduce reactivity, and build healthier communication habits, especially in families where enmeshment or cutoff patterns have existed for generations.
4. Corrective Emotional Experiences
Through carefully designed conversations, therapeutic dialogues, or couple sessions, therapists create opportunities for clients to experience relationships differently. This can gradually shift long-standing emotional expectations or fears inherited from earlier generations.
5. Narrative Redefinition
Families often arrive with stories like “We don’t express emotions,” “The firstborn always sacrifices,” or “Conflict destroys relationships.” Narrative interventions help clients rewrite these inherited scripts into healthier, more empowering ones, changing outcomes for future generations.
6. Pattern Recognition as a Change Tool
Rather than stopping at identification, therapists actively use pattern recognition to guide specific interventions. Seeing the pattern visually, whether through a genogram, timeline, or system map, helps clients understand what they’re repeating, why it matters, and what needs to shift. This insight becomes a practical plan for change, not just an observation.
7. Integrating Visual Tools Into Intervention
Visual tools like genograms allow therapists to layer emotional patterns, relational histories, and traumatic events all in one place. These visuals become intervention tools themselves, helping clients stay grounded, reducing overwhelm, and making complex histories easier to work through collaboratively.
Make Transgenerational Therapy Clearer With Visual Mapping
Transgenerational Therapy becomes significantly more effective when patterns, roles, and emotional histories can be seen, not just discussed. Visual mapping tools like genograms help therapists move from scattered information to structured insights, making deep family work faster, clearer, and more intuitive. If you want a workspace that supports this level of clarity, Creately is designed to make mapping family systems effortless. Therapists love how simple it is to customize genograms, organize multi-session histories, and collaborate visually. Explore our ready-to-use templates and see how Creately can bring greater insight, speed, and structure to your transgenerational therapy workflow.