Starting a business can feel overwhelming, with countless decisions to make and uncertainties to navigate. The Lean Business Model Canvas helps entrepreneurs focus on what truly matters—understanding customers, testing ideas quickly, and iterating on solutions without wasting time or resources. In this guide, we’ll walk you through a practical approach to using the canvas effectively, offering tips, examples, and strategies to turn your ideas into actionable plans.
Lean Canvas Definition
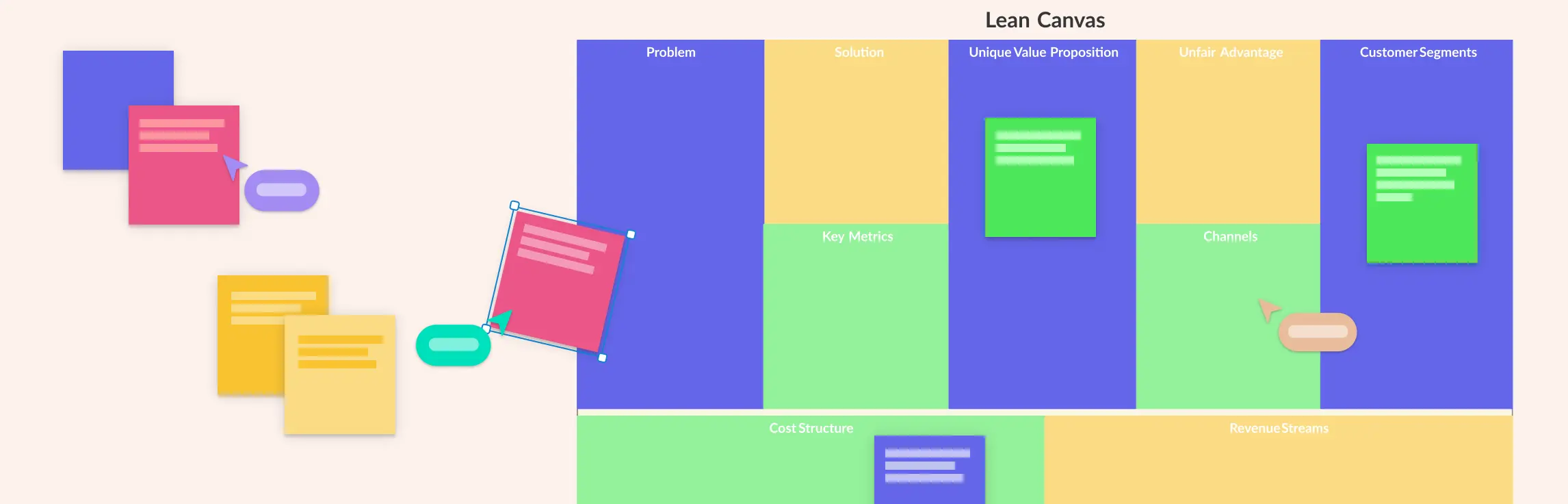
The Lean Business Model Canvas is a one-page framework that helps entrepreneurs map out and test the key elements of their business idea quickly and efficiently. The Lean Canvas focuses on the essentials—identifying customer problems, proposing solutions, understanding market segments, and figuring out how the business will make money. It’s designed to help startups experiment, learn, and iterate without wasting time or resources, making it easier to validate ideas before investing heavily.
History of the Lean Canvas
The Lean Canvas was adapted from Alex Osterwalder’s original Business Model Canvas by Ash Maurya. Maurya’s version is specifically tailored for lean startups, emphasizing speed, flexibility, and problem-solving over lengthy documentation.
What is the purpose of a Lean Canvas
Provides a clear, one-page overview of your business idea.
Helps identify customer problems and target market segments.
Encourages testing assumptions quickly to reduce risk.
Focuses on solutions and revenue streams for practical planning.
Supports iterative learning and adapting your business step by step.
What to Include in the Lean Canvas: Key Elements
1. Problem
Think of the main issues your customers face. For example, if you want to start a food delivery service, the problems might be “people don’t have time to cook,” or “restaurants take too long to deliver.” Listing 1–3 big problems helps you focus on what your business is actually solving.
2. Customer Segments
These are the people who experience the problems you just listed. Who will use your product or service? Are they busy parents, college students, or office workers? Knowing your audience helps you design solutions that really work for them.
3. Unique Value Proposition (UVP)
This is a simple statement that explains why your idea is special. Ask yourself: “Why would someone pick my solution instead of the alternatives?” For example, “fastest and healthiest meals delivered to your door in 20 minutes” clearly shows what makes your business different.
4. Solution
Now that you know the problem, describe how your product or service solves it. Keep it simple. For the food delivery example, the solution could be a mobile app that connects users to nearby healthy restaurants with guaranteed quick delivery.
5. Channels
Channels are the ways you reach your customers. How will they hear about your solution and get it? This could be social media, a website, an app, email, or even physical stores. Choosing the right channels ensures your solution reaches the people who need it.
6. Revenue Streams
How will your business make money? Will customers pay per product, subscribe monthly, or will you earn through ads? For our food delivery example, you could charge delivery fees, partner with restaurants for commissions, or offer subscription meal plans.
7. Cost Structure
This is all about the money you need to run your business. Think salaries, software, marketing, and delivery costs. Understanding your costs helps you know how much money you need and whether your business can be profitable.
8. Key Metrics
Metrics are numbers that show if your business is working. What will you track to know you’re succeeding? It could be the number of users, deliveries per day, customer satisfaction, or monthly revenue. These numbers help you make smarter decisions.
9. Unfair Advantage
This is something that sets you apart and is hard for others to copy. It could be a special technology, an exclusive partnership, or a loyal community. For example, having a network of local chefs who only work with your app can be an unfair advantage over competitors.
How to Make a Lean Canvas
Step 1: Start with a Problem You Want to Solve
Don’t worry about the whole business yet. Pick one problem you care about solving and think about who struggles with it the most. This keeps your focus sharp and prevents getting overwhelmed.
Creately tip: Use Lean Canvas templates to get started quickly. You can also combine it with flowcharts, mind maps, empathy maps, or journey maps to explore ideas, understand customer needs, and add context to your canvas.
Step 2: Make Quick Hypotheses
Write down assumptions about your customers, solutions, and how you might make money. Think of them as “guesses” you can test later. The Lean Canvas is about experimenting, not being perfect from the start.
Creately tip: Use sticky notes to organize your hypotheses visually. You can also bring in relevant data, research findings, or notes directly onto the canvas in Creately, which helps consolidate information for brainstorming and makes it easier to see patterns and connections between problems, solutions, and potential revenue streams.
Step 3: Prioritize and Fill Out the Canvas
Use your hypotheses to fill the canvas. Focus first on the areas that are most uncertain—usually problems, solutions, and customers. The goal is to see where you need real-world validation first.
Creately tip: Take advantage of real-time collaboration to work with your team. Add notes and comments, and use voting or a prioritization matrix to decide which assumptions or ideas to tackle first. Sharing the canvas with stakeholders using sharing options keeps everyone aligned.
Step 4: Test Your Ideas Fast
Talk to real customers, run surveys, or create simple prototypes. Check if your assumptions are correct. If something doesn’t work, update your canvas and try again. The Lean Canvas is a living document, not a final plan.
Creately tip: Use presentation mode in Creately’s Lean Canvas template to showcase your Lean Canvas clearly to your team or stakeholders. You can also collect feedback directly on the canvas, create surveys, and consolidate survey responses to spot patterns and insights. This makes it easy to analyze results and refine your ideas quickly.
Step 5: Iterate and Improve
Keep refining your canvas as you learn. Each iteration should bring you closer to a business model that actually works. Over time, you’ll have a clear, validated roadmap for your startup.
Creately tip: Combine your Lean Canvas with task tracking features, like visual Kanban boards, timelines, or to-do lists, to assign follow-up actions and track progress. Use version history to review past iterations and see how ideas evolved over time.
Lean Canvas Best Practices
Start with the problem: Focus on the most pressing customer problems before solutions to ensure your idea addresses real needs.
Keep it simple and visual: Use concise statements, colors, shapes, and connectors to make your canvas clear and easy to understand.
Validate and prioritize assumptions: Treat each section as a hypothesis, and focus on high-uncertainty areas like problem, solution, and customer segments first.
Iterate continuously: Update the canvas as you gather feedback, learn from experiments, and refine your ideas.
Collaborate with your team: Involve multiple perspectives, use feedback, and leverage brainstorming to improve assumptions.
Combine with other tools: Use mind maps, journey maps, or flowcharts to explore context, processes, and customer insights alongside your canvas.
Real-World Lean Canvas Examples
Seeing the Lean Canvas in action makes it easier to understand how startups use it to map, test, and refine business ideas. Below are simplified examples of three successful companies showing how each element can be applied in real life.
1. Airbnb
Airbnb identified the high cost of traditional hotels and the desire for authentic travel experiences. Their Lean Canvas shows how they created a platform for renting spare rooms, offering affordable stays while building a trusted host network.
2. Amazon
Uber focused on the problem of finding reliable, convenient, and affordable transportation. Their Lean Canvas highlights a ride-hailing app connecting drivers and riders, with a large network as their unfair advantage and a simple, user-friendly mobile app as their key channel.
3. Uber
Amazon started by solving the limited access to books locally. Their Lean Canvas demonstrates how an online bookstore with efficient logistics and strong customer service became a scalable business model, eventually expanding to a wide range of products.
Free Lean Business Canvas Templates
Now that you know what is a lean canvas and how to create one, here are some ready-to-use templates to get started.
Startup Lean Canvas
Blank Lean Canvas
Facebook Lean Canvas
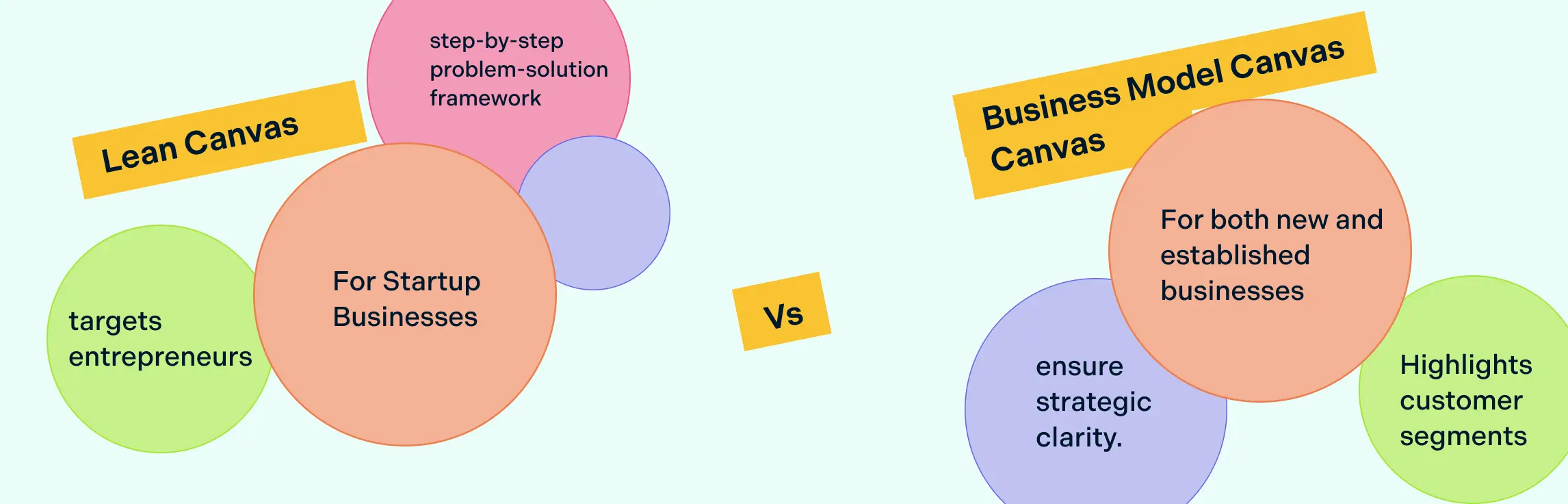
Lean Canvas vs. Business Model Canvas
The Lean Canvas is a startup-focused version of the Business Model Canvas. It swaps traditional elements like key partners and key resources for more practical ones like problem, solution, key metrics, and unfair advantage. While the Business Model Canvas helps established companies plan and refine their overall strategy, the Lean Canvas helps entrepreneurs test and validate ideas quickly.
| Aspect | Lean Canvas | Business Model Canvas |
| Purpose | Validating and testing startup ideas | Structuring and managing established businesses |
| Focus | Problems, solutions, assumptions, and metrics | Operations, partners, and long-term strategy |
| Key Elements | Problem, Solution, Key Metrics, Unfair Advantage | Key Partners, Key Resources, Key Activities |
| Best For | Startups and early-stage ventures | Established or scaling businesses |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lean Canvas
The Lean Canvas is a powerful tool for startups to map out and test business ideas quickly. Like any tool, it comes with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding both can help entrepreneurs use it effectively and know when to complement it with other planning methods.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Quick and simple: Capture the core business idea in minutes. | Not detailed: Lacks in-depth financials and long-term strategy. |
| Focus on problems and solutions: Helps identify what matters to customers. | May oversimplify: Complex businesses may need more tools. |
| Encourages experimentation: Test assumptions early to reduce risk. | Needs validation: Without testing, it’s just ideas. |
| Visual and easy to understand: Provides a clear snapshot for teams and stakeholders. | Limited investor appeal: Lacks full financial projections. |
| Highlights risks early: Focuses on uncertainties before major investments. | Misses operational details: Key partners, resources, and processes aren’t fully covered. |
| Supports collaboration: Teams can brainstorm and iterate in real time. | High-level only: Best combined with other planning tools for a full picture. |
FAQs About the Lean Canvas
What is the Lean Startup Methodology?
Why should product managers use a Lean Business Canvas?
When to use a Lean Canvas in product development?
Do I need a team to create a Lean Canvas?
Can Lean Canvas be used for existing businesses?
Why is the Lean Canvas popular among startups?
What common mistakes should I avoid?
How do I measure success using a Lean Canvas?